Leverage Turing Intelligence capabilities to integrate AI into your operations, enhance automation, and optimize cloud migration for scalable impact.
Advance foundation model research and improve LLM reasoning, coding, and multimodal capabilities with Turing AGI Advancement.
Access a global network of elite AI professionals through Turing Jobs—vetted experts ready to accelerate your AI initiatives.
Leverage Turing Intelligence capabilities to integrate AI into your operations, enhance automation, and optimize cloud migration for scalable impact.
Advance foundation model research and improve LLM reasoning, coding, and multimodal capabilities with Turing AGI Advancement.
Access a global network of elite AI professionals through Turing Jobs—vetted experts ready to accelerate your AI initiatives.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: What’s the difference? IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS have gained tremendous popularity in recent years owing to the benefits they offer businesses of all sizes. These cloud computing service models provide organizations with cost-effective, scalable, and flexible solutions that can be tailored to their specific needs.
In this blog post, we will explore the key differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, their key characteristics, pros and cons, use cases, key differences, and examples. We will also discuss when to use each service to help you make informed decisions for your business.
Let’s get started.
What are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Let’s understand the basics.
What is IaaS?
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) is a cloud computing service model that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. In this model, a third-party provider hosts hardware, software, servers, storage, and other infrastructure components on behalf of its users. IaaS is highly scalable and allows businesses to purchase resources on-demand, making it an ideal solution for temporary, experimental, or changing workloads.
Also, read: Infrastructure as Code (IaC): A Beginner’s Guide 2024
What is PaaS?
PaaS (Platform as a Service) is a cloud computing service model that provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS includes tools, libraries, and services that enable developers to create and manage applications more efficiently. This model allows businesses to focus on developing their applications while the PaaS provider takes care of infrastructure management.
What is SaaS?
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud computing service model that delivers software applications over the Internet. With SaaS, users can access software applications through a web browser, eliminating the need for installing and maintaining software on individual devices. SaaS providers manage the underlying infrastructure, ensuring that the applications are always up-to-date and available.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Characteristics

Characteristics of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s understand the key characteristics of each.
IaaS Characteristics
The key characteristics of IaaS include
- Scalability: IaaS offers on-demand resources, allowing businesses to scale up or down as needed.
- Cost-effective: Users only pay for the resources they consume, reducing upfront costs.
- Customization: IaaS provides a high level of control over the infrastructure, enabling businesses to tailor their environment to their specific needs.
- Security: IaaS providers typically offer robust security measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection, and encryption.
PaaS Characteristics
The key characteristics of PaaS include:
- Developer tools: PaaS includes a suite of tools and services designed to streamline application development and deployment.
- Middleware: PaaS provides middleware services, such as database management, messaging, and caching, to support application development.
- Scalability: PaaS platforms can automatically scale resources to accommodate changing workloads.
- Collaboration: PaaS enables developers to collaborate on projects more easily, as they can access the same tools and resources from anywhere.
SaaS Characteristics
The key characteristics of SaaS include:
- Accessibility: SaaS applications are accessible from any device with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote work.
- Automatic updates: SaaS providers handle software updates, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
- Subscription-based pricing: SaaS typically uses a subscription pricing model, allowing businesses to pay for only the features they need.
- Integration: SaaS applications often integrate with other cloud services, streamlining workflows and data sharing.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Pros and Cons

IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: Pros and Cons
In order to understand these cloud computing service models better, it’s essential to make a note of their pros and cons.
IaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Flexibility: IaaS offers businesses the flexibility to scale resources up or down as needed.
- Cost savings: IaaS eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own hardware, reducing capital expenses.
- Control: IaaS provides businesses with control over their infrastructure, allowing them to customize their environment to meet their specific needs.
Cons:
- Management: IaaS requires businesses to manage their infrastructure, which can be time-consuming and complex.
- Security: While IaaS providers offer security measures, businesses are still responsible for securing their applications and data.
PaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Faster development: PaaS provides tools and services that streamline application development, enabling developers to build and deploy applications more quickly.
- Reduced complexity: PaaS abstracts the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on writing code rather than managing servers and networks.
- Cost savings: PaaS eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own development infrastructure.
Cons:
- Limited customization: PaaS platforms may not offer the same level of customization as IaaS, which can be a drawback for businesses with unique requirements.
- Vendor lock-in: Businesses may become dependent on a specific PaaS provider, making it difficult to switch platforms or migrate applications.
SaaS Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Ease of use: SaaS applications are easy to use and require no installation or maintenance, making them ideal for businesses with limited IT resources.
- Cost savings: SaaS eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own software, reducing capital expenses.
- Automatic updates: SaaS providers handle software updates, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
Cons:
- Limited customization: SaaS applications may not offer the same level of customization as IaaS or PaaS, which can be a drawback for businesses with unique requirements.
- Data security: While SaaS providers typically offer robust security measures, businesses must still trust the provider to protect their sensitive data.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Use Cases and Examples
Here are some of the most common examples of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
IaaS Use Cases and Examples
- Big data analysis: IaaS provides the scalable resources needed to process and analyze large datasets, making it ideal for big data projects. Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2.
- Backup and disaster recovery: IaaS enables businesses to store backups and implement disaster recovery solutions in the cloud, ensuring data protection and business continuity. Example: Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
Also, read: Azure vs AWS: Which is Better?
- Web hosting: IaaS provides the infrastructure needed to host websites and web applications, offering scalability and flexibility. Example: Google Cloud Compute Engine.
PaaS Use Cases and Examples
- Application development: PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications quickly and efficiently. Example: Heroku.
- Internet of Things (IoT) development: PaaS offers tools and services that support IoT development, enabling businesses to create and manage connected devices. Example: IBM Watson IoT Platform.
- Microservices architecture development: PaaS supports the development and deployment of microservices, allowing businesses to build modular, scalable applications. Example: Red Hat OpenShift.
SaaS Use Cases and Examples
- Customer relationship management (CRM): SaaS CRM solutions enable businesses to manage customer data, track interactions, and analyze customer behavior. Example: Salesforce.
- Project management: SaaS project management tools help teams collaborate, track progress, and manage resources more effectively. Example: Trello.
- Human resources management (HRM): SaaS HRM solutions streamline HR processes, such as recruiting, onboarding, and benefits administration. Example: Workday.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: When to Use IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
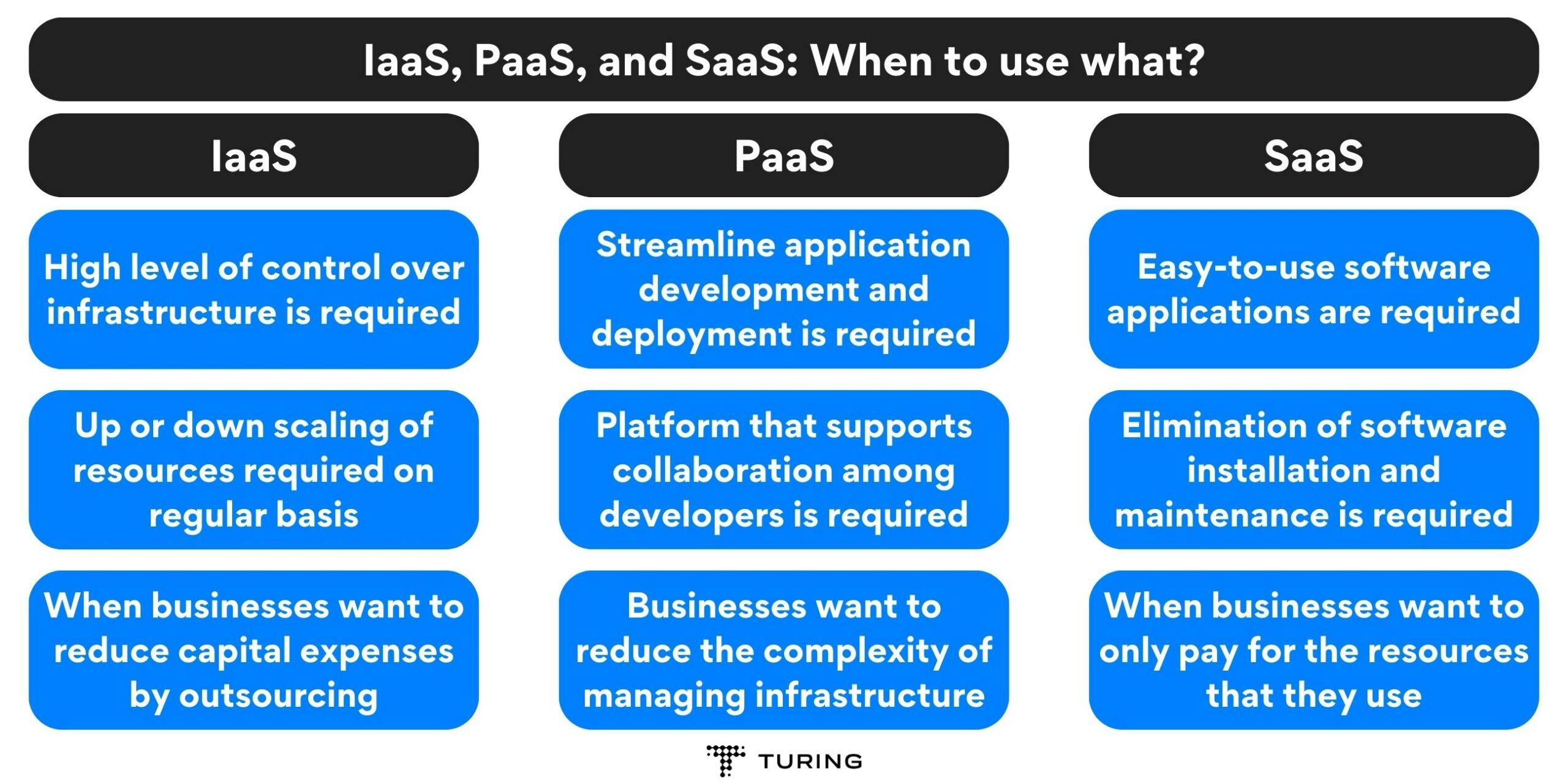
When to use IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Each of these cloud computing service models has different use cases. Let’s take a look at them one by one.
When to use IaaS:
- When businesses require a high level of control over their infrastructure.
- When businesses need to scale resources up or down quickly to accommodate changing workloads.
- When businesses want to reduce capital expenses by outsourcing hardware and infrastructure management.
When to use PaaS:
- When businesses want to streamline application development and deployment.
- When businesses need a platform that supports collaboration among developers.
- When businesses want to reduce the complexity of managing infrastructure.
When to use SaaS:
- When businesses require easy-to-use software applications that are accessible from any device.
- When businesses want to eliminate the need for software installation and maintenance.
- When businesses prefer a subscription-based pricing model that allows them to pay for only the features they need.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Key Differences
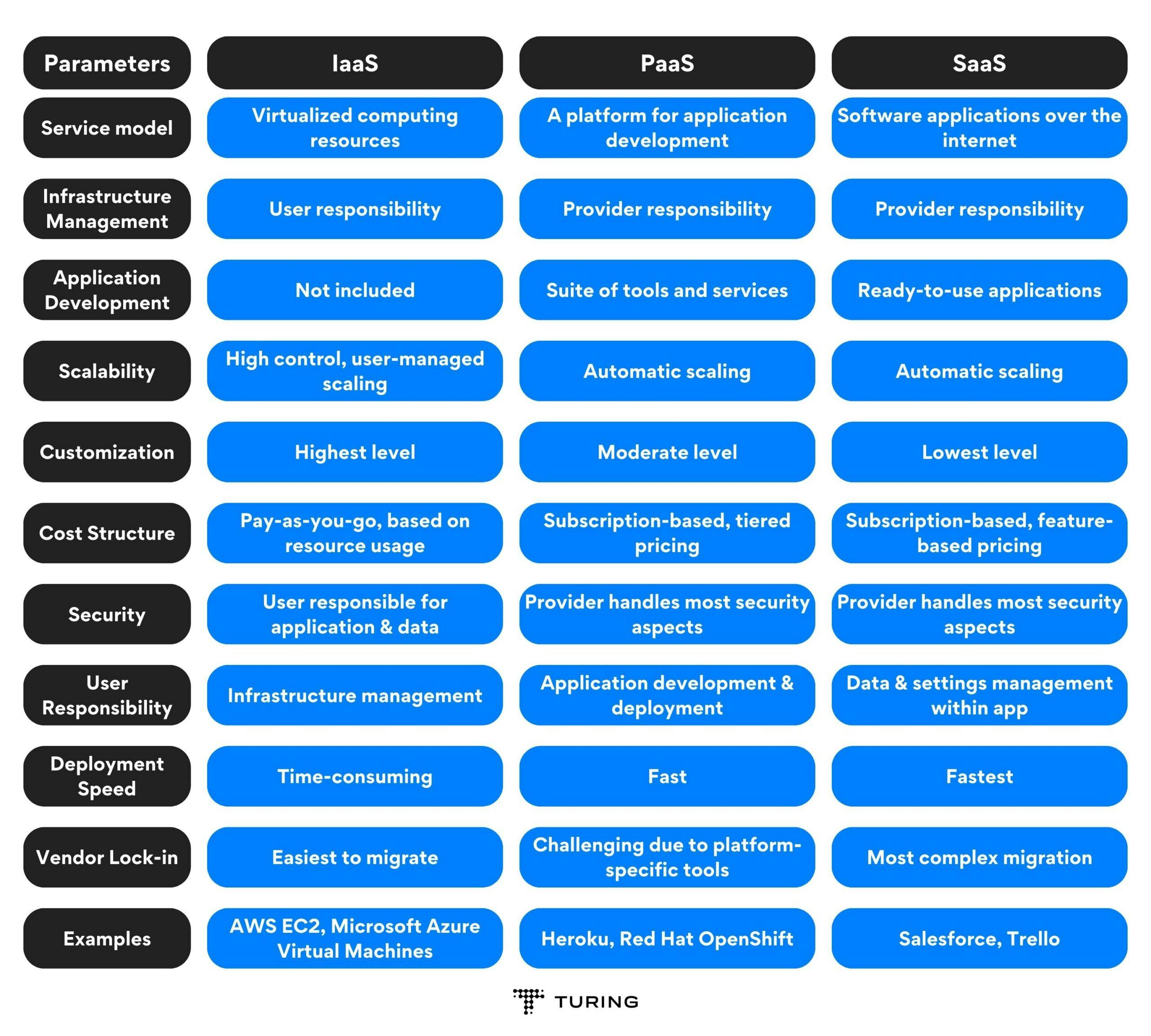
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Key Differences
The key differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS can be understood by comparing them across various parameters. Here, we will discuss 10 different parameters to highlight the distinctions between these cloud computing service models.
- Service Model: IaaS provides virtualized computing resources, PaaS offers a platform for application development, and SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet.
- Infrastructure Management: IaaS users are responsible for managing their infrastructure, while PaaS and SaaS users rely on the provider for infrastructure management.
- Application Development: IaaS does not include tools for application development, whereas PaaS provides a suite of tools and services for developers. SaaS focuses on delivering ready-to-use applications.
- Scalability: All three models offer scalability, but IaaS provides the most control over resource allocation, while PaaS and SaaS handle scaling automatically based on user demand.
- Customization: IaaS offers the highest level of customization, allowing users to tailor their infrastructure to their needs. PaaS offers some customization options, while SaaS typically has the least customization capabilities.
- Cost Structure: IaaS follows a pay-as-you-go model, where users pay for the resources they consume. PaaS usually has a subscription-based pricing model, with different tiers based on resource usage. SaaS also uses a subscription-based pricing model, with plans based on features and the number of users.
- Security: IaaS users are responsible for securing their applications and data, while PaaS and SaaS providers handle most security aspects, including infrastructure and application security.
- User Responsibility: IaaS users are responsible for managing their infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking. PaaS users focus on application development and deployment, while SaaS users only need to manage their data and settings within the application.
- Deployment Speed: IaaS deployment can be time-consuming, as users need to set up and configure their infrastructure. PaaS enables faster deployment, as the platform is already set up for development. SaaS offers the quickest deployment, as users can access applications immediately through a web browser.
- Vendor Lock-in: IaaS users can easily migrate their infrastructure to another provider, while PaaS users may face challenges due to platform-specific tools and services. SaaS users may experience the most vendor lock-in, as migrating data and settings between applications can be complex.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS Diagram
To visualize the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, imagine a three-layered diagram:
- IaaS: The bottom layer represents the infrastructure, including hardware, servers, storage, and networking components.
- PaaS: The middle layer represents the platform, including tools, libraries, and services that support application development.
- SaaS: The top layer represents the software applications that users access through a web browser.

SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS diagram
Summary
In summary, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are three distinct cloud computing service models that offer businesses various levels of control, customization, and management. By understanding the key differences between these models, their characteristics, pros and cons, use cases, and examples, businesses can make informed decisions about which cloud service is best suited to their needs.
If you’re looking to hire developers skilled in IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS, try Turing. Hire the top 1% of the 3 million developers in Turing’s talent pool in just 4 days.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources, PaaS offers a platform for application development, and SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet. IaaS users manage their infrastructure, PaaS users focus on application development, and SaaS users only need to manage their data and settings within the application.
2. How do I choose between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS for my business?
Consider your business requirements, the level of control and customization you need, and your IT resources. Choose IaaS if you need control over infrastructure, PaaS for streamlined application development, and SaaS for ready-to-use applications with minimal management.
3. What are the cost structures for IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
IaaS follows a pay-as-you-go model based on resource usage, PaaS uses subscription-based tiered pricing, and SaaS offers subscription-based pricing based on features and the number of users.
4. How do IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS handle scalability?
All three models offer scalability, but IaaS provides the most control over resource allocation, while PaaS and SaaS handle scaling automatically based on user demand.
5. Are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS secure?
IaaS users are responsible for securing their applications and data, while PaaS and SaaS providers handle most security aspects, including infrastructure and application security. However, businesses should still evaluate the security measures provided by their chosen cloud service provider.
6. What are some examples of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS providers?
IaaS examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 and Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines. PaaS examples are Heroku and Red Hat OpenShift. SaaS examples include Salesforce and Trello.
7. Can I use a combination of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS for my business?
Yes, many businesses use a hybrid approach, combining different cloud service models to meet their specific needs. For example, a company might use IaaS for its infrastructure, PaaS for application development, and SaaS for specific software applications.
8. What is vendor lock-in, and how does it affect IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS users?
Vendor lock-in occurs when a business becomes dependent on a specific provider, making it difficult to switch platforms or migrate applications. IaaS users can more easily migrate their infrastructure, while PaaS users may face challenges due to platform-specific tools. SaaS users may experience the most vendor lock-in, as migrating data and settings between applications can be complex.
9. How do IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS impact deployment speed?
IaaS deployment can be time-consuming, as users need to set up and configure their infrastructure. PaaS enables faster deployment, as the platform is already set up for development. SaaS offers the quickest deployment, as users can access applications immediately through a web browser.
10. What are the main advantages of using cloud services like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Cloud services offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and reduced IT management. IaaS provides control over infrastructure, PaaS streamlines application development, and SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications with minimal management.
Ashwin Dua
Sanika
Want to accelerate your business with AI?
Talk to one of our solutions architects and start innovating with AI-powered talent.



