JSON: Introduction, Benefits, Applications, and Drawbacks
•4 min read
- Languages, frameworks, tools, and trends

In modern times, all software applications, be it web, desktop or mobile, rely on one of the two most popular data-interchange formats: JSON and XML. Some of the other data exchange formats include YAML and CSV. All of these formats define a set of rules to represent and transmit data across applications, servers, operating systems, etc.
In this article, we will discuss the JSON format in detail and answer some of the questions like:
- What was the server's burden?
- How did JSON help servers sort out all that mess single-handedly?
- Why do you need to use the JSON format?
What is JSON file format?
JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is a lightweight, text-based, data-interchange format that follows JavaScript object syntax. JSON is used for data transportation and restoration in places of XML structures. The JSON format is often used when data is sent from a server to a web page or a browser for rendering.
Even though JSON format is derived from JavaScript object structure, it is text-only and can be used independently from JavaScript. Several programming languages, such as Python, Java, C++, etc., can access and support JSON format.
What does a JSON format look like?
JSON file structure is built on these two structures-
- A collection of name/value pairs
- An ordered list of values
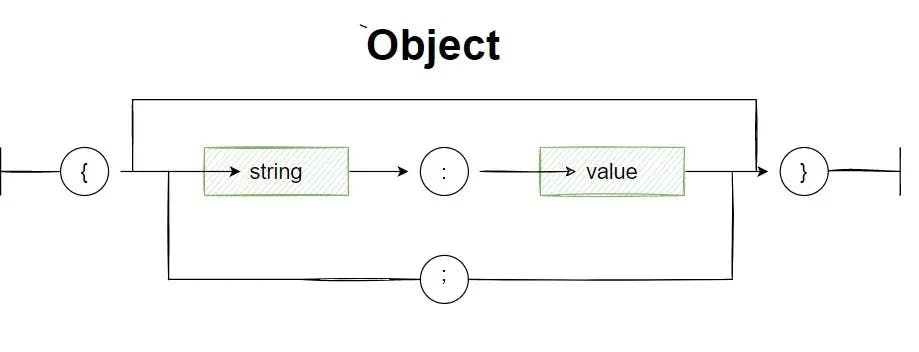
JSON format: Object
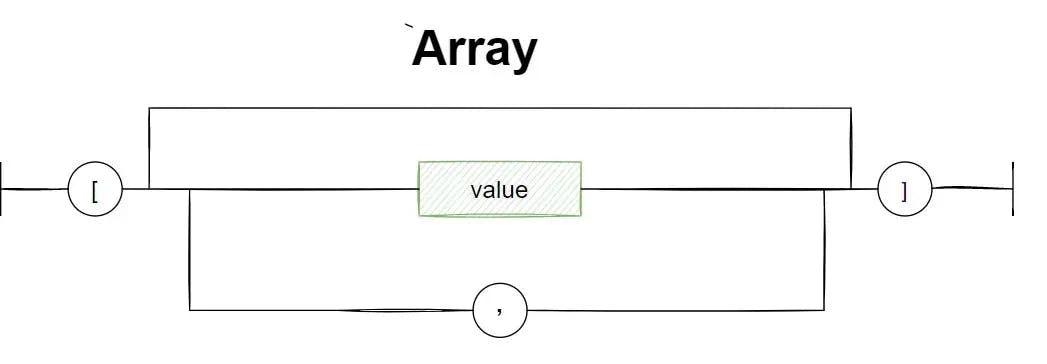
JSON format: Array
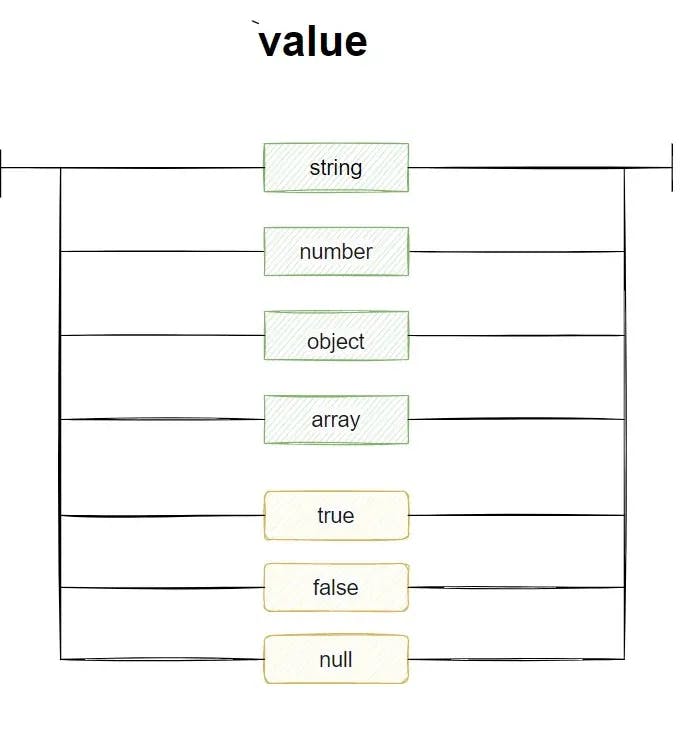
JSON format: Value
JSON format: Syntax and example
The biggest advantage of JSON file format is its structure and syntax rules. These features give JSON an upper hand over classical formats like XML. The simplest form of JSON structure follows this set of rules-
- Data must be in name & value pairs
- Data separation must be done using commas
- Curly brackets hold the objects as a whole
- Square brackets hold the complete array
Here’s what a typical JSON format example looks like, following the above syntax rules.
{
“turingemp”:[
{“firstname”: “Michel”, “lastname”: “Stark”},
{“firstname”: “Peter”, “lastname”: “Parker”},
{“firstname”: “David”, “lastname”: “Book”},
{“firstname”: “Pyaare”, “lastname”: “Mohan”}
]
}Explanation -
In the above example-
Names are “firstname” and “lastname,” while values are “Michel”, “Peter”, “David” etc.
Data separation- {“firstname”: “Michel” “lastname”: “Stark”},
Why should you use a JSON format?
A genuine question that strikes most developers is, why use JSON data format when we had/have other options like YAML, XML, etc.? The answer lies in the history of client-server communication itself.
Until a few decades ago, the communication between client and server was inefficient, as the server was overburdened with a heavy workload. For example, your web browser was only supposed to render things like outcomes of a web page search or any query result without any backend technicalities. The rest of the work from processing requests to forwarding them was weighed on the server.
Thus, a lightweight and text-based structure like JSON format was needed to solve all these problems.
Let’s have a look at some of the characteristics of the JSON data format that helps millions of developers across the world.
JSON format: Characteristics
- Server parsing is easy in JSON data format. However, the parser at that moment should not be a common activity.
- Easy to manipulate
- Better schema support
- Self-describing
- JSON is faster
JSON format vs other formats
JSON vs XML
The JSON format is easy to understand and read compared to XML. This is one of the reasons why JSON is preferred over XML.
XML format example -
<turingemp>
<turingemp>
<firstName>Tin</firstName> <lastName>Cook</lastName>
</turingemp>
<turingemp>
<firstName>Elon</firstName> <lastName>Must</lastName>
</turingemp>
<turingemp>
<firstName>Mark</firstName> <lastName>Iceberg</lastName>
</turingemp>
<turingemp>
<firstName>Atisundar</firstName> <lastName>Pichai</lastName>
</turingemp>
</turingemps>JSON vs CSV
The JSON file format can easily handle unstructured, complex data, which is not possible with CSV format. In addition to that, hierarchical data can be easily represented using JSON, unlike the CSV format. Hence, JSON is more versatile than the CSV format.
What are the applications of JSON format?
The most desired and popular applications of JSON are listed below:
- It can be used with various modern programming languages such as Python, Ruby, Java, etc.
- It is used for data transmission between a server and web applications
- JSON is used in JS-based applications, for example- web browser extensions and websites.
- APIs and web services use the JSON format for providing public data.
- JSON data format simplifies complex data by converting the data extraction process into a meaningful and predictable JSON file format.
Limitations of JSON format
- No error handling - JSON has no error handling mechanism for JSON calls. Error handling also depends on the dynamic script insertion. If dynamic script insertion is not there, the code might fail.
- No comments - These two words are enough to make the developer’s life difficult.
- Security - JSON can be dangerous if used with untrusted browsers or services. JSON service returns a JSON response, which the browser uses directly, and if the browser is not secure, it can be hacked. Thus, it makes web services vulnerable to different kinds of cyberattacks.
- No date type - There can be some anomalies in a string representation of dates.
- Robustness - JSON is not as robust as an XML data structure. This limitation is mainly due to the lack of standardized availability of schemas.
JSON format: Closing notes
We can undoubtedly conclude that JSON is here to stay and it's significant for a developer to learn and understand its efficiency. Therefore, every developer should try their hands on JSON to easily transmit structured data across platforms and operating systems.

Author
Abhishek Jaiswal
Abhishek is a Geek by day and Batman by night. He loves to talk about Data and his passion encircles around Trekking, Hitch Hiking, Gardening, and analyzing Ancient Indian Texts. His geeky stuff got highlighted at Microsoft, Code Project, C-sharp Corner, etc. For more info, either catch up with him for a cup of coffee or reach out to him on LinkedIn | Twitter | GitHub