Blockchain for Supply Chain: Paving the Way for Transparency and Efficiency

Huzefa Chawre
•11 min read
- AI/ML
Blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer in supply chain management, revolutionizing how businesses track, verify, and secure their transactions. With its decentralized and immutable nature, blockchain offers unprecedented transparency, efficiency, and trust in supply chain processes.
From enhancing traceability and reducing fraud to optimizing inventory management and streamlining logistics, blockchain has the potential to reshape the supply chain landscape. With the supply chain being a critical component of business operations, integrating it with blockchain technology offers a new paradigm forward.
According to research findings published on PRNewswire, the projected value of blockchain technology in supply chain management will likely be around USD 3153.7 Million by 2028. The market for blockchain in supply chains is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 51.3% between 2022 and 2028.
So, what are the different use cases of blockchain for supply chains? And what are the prominent benefits and challenges of implementing blockchain for supply chain management? This blog comprehensively answers these questions and offers a thorough guide on blockchain supply chain management.
Let’s get started!
Blockchain use cases in supply chain management
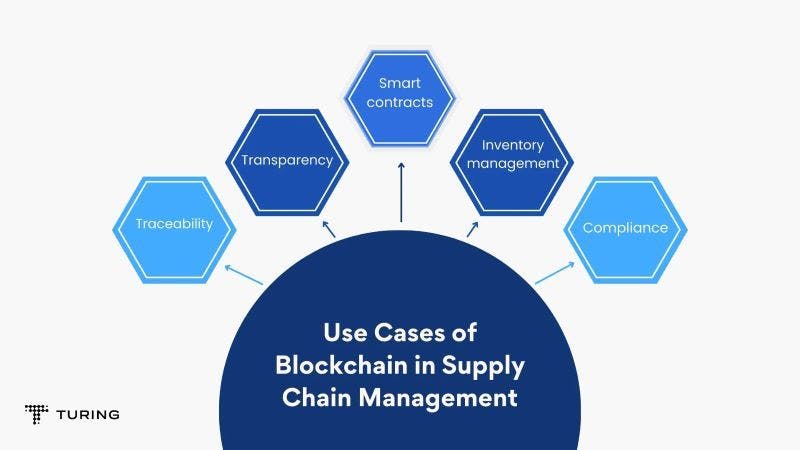
The prominent use cases of blockchain for supply chain management include:
1. Traceability
Traceability is one of blockchain's most compelling use cases in supply chain management. Blockchain empowers businesses to create an immutable ledger of every product's journey, from its origin to its final destination. With blockchain's transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping, companies can trace the movement of goods with unparalleled accuracy.
The high level of traceability enhances accountability and serves as a critical tool for product recalls and quality assurance. The consumers also gain deeper insight into the origins of the products they purchase, fostering trust and strong relationships with the companies.
2. Transparency
Transparency is a significant use case of blockchain for supply chain management. Traditional supply chains often suffer from a lack of visibility and trust among participants. Blockchain technology addresses this challenge by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger that all stakeholders can access and verify.
Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is transparent and cannot be altered, ensuring a single source of truth for all involved parties. This transparency enables real-time tracking of goods, from raw materials to the end product, allowing businesses to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and potential areas for improvement.
3. Smart contracts
Smart contracts represent a transformative use case of blockchain technology in supply chain management. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions encoded on the blockchain. These contracts automate and streamline various supply chain processes, such as procurement, payments, and compliance.
By leveraging blockchain's decentralized and transparent nature, smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reduce administrative costs, and minimize the risk of errors or disputes.
For instance, when a shipment reaches a specific location, the smart contract can automatically trigger the payment to the supplier. This automation improves efficiency and enhances accountability among supply chain participants, ensuring fulfillment of contractual obligations.
4. Inventory management
Inventory management represents a crucial use case for blockchain technology in supply chain management. Traditional inventory management systems often suffer from inefficiencies, inaccuracies, and a lack of real-time visibility. Blockchain addresses these challenges by providing a secure and transparent ledger that tracks the movement and status of inventory items across the supply chain.
Through IoT devices and sensors, real-time data can be recorded on the blockchain, allowing stakeholders to accurately monitor inventory levels, locations, and conditions. This transparency reduces the risk of overstocking or stockouts and helps to optimize supply chain operations.
5. Compliance
With its immutable and transparent nature, blockchain provides a reliable and auditable record of all transactions and activities throughout the supply chain. This data enables businesses to demonstrate compliance with various regulations, standards, and certifications.
By securely storing and sharing data on the blockchain, supply chain participants can easily verify the authenticity and integrity of documents, such as certificates of origin, quality inspections, and regulatory compliance records.
Blockchain also facilitates the automation of compliance processes through smart contracts, ensuring that all parties adhere to predefined rules and regulations. By leveraging blockchain for compliance, businesses can mitigate risks, improve regulatory reporting, and enhance trust among stakeholders in the supply chain ecosystem.
Blockchain industry applications
Blockchain is widely used in numerous industries to enhance supply chain operations through increased transparency, visibility, compliance, and collaboration. The prominent companies that use blockchain for supply chain management include IBM, Walmart, FedEx, British Airways, DHL, and Nestle, among others.
Here, we explore prominent industrial applications for blockchain in supply chain management.
1. Food and agriculture
In food and agriculture, blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool to address critical challenges such as food safety, traceability, and transparency. By documenting each stage of the process from farm to table on an immutable ledger, blockchain guarantees that consumers can access accurate information about the origin of their food products. This accessibility helps rapidly and accurately identify food sources and encourages responsible farming practices.
For example, the IBM Food Trust blockchain platform is used by food companies to track the movement of food products across their supply chains. This information can be accessed by all participants in the supply chain, improving transparency and traceability.
Additionally, blockchain can help track and monitor the conditions in which food is produced, transported, and stored, ensuring compliance with regulations and promoting sustainable practices.
2. Healthcare
The healthcare industry has embraced blockchain technology to address issues like data integrity, patient privacy, and drug traceability. By leveraging blockchain, healthcare organizations can track the movement of pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and supplies from manufacturers to patients, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeit products. This also expedites the tracking of medicines during recalls.
For example, Mediledger is a company that uses blockchain to track prescription drug movement. This tracking prevents counterfeit drugs and ensures that patients receive the right medication. Ultimately, blockchain safeguards patient information, enhances drug safety, and improves supply chain management efficiency in the healthcare industry.
3. Retail
Blockchain technology has significantly impacted the retail industry by addressing issues like counterfeit products, supply chain inefficiencies, and consumer trust. Besides providing advanced traceability, blockchain facilitates efficient inventory management by providing real-time visibility into stock levels, enabling retailers to optimize replenishment and reduce stockouts.
For example, the Walmart Food Traceability Initiative uses blockchain to track the movement of leafy green vegetables in its supply chain network. This tracking ensures these products are not contaminated and safe to eat.
4. Automotive
In the automotive industry, blockchain helps streamline the complex web of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, reducing paperwork and administrative burdens. Smart contracts automate various processes, including payments and compliance checks, fostering collaboration and efficiency across the automotive supply chain.
Additionally, by leveraging blockchain, automotive manufacturers can track the entire lifecycle of a vehicle, from sourcing raw materials to the assembly process and delivery to the end customer.
For example, BMW uses blockchain to track the movement of cobalt, a mineral used in the batteries of electric vehicles. This tracking helps ensure that the cobalt is mined responsibly and does not come from conflict zones.
Blockchain benefits in supply chain management
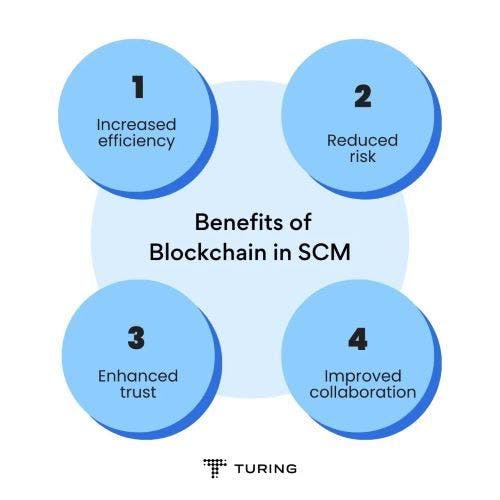
Blockchain offers tangible benefits to businesses across different sectors and is emerging as a critical lever in streamlining supply chain operations. Blockchain builds on top of existing systems and provides significant value for businesses by increasing efficiency, enhancing trust, and building a more robust collaboration between various stakeholders involved in supply chain operations.
Let us explore the strategic benefits offered by blockchain for supply chain management.
1. Increased efficiency
The traditional supply chains often involve multiple intermediaries, manual record-keeping, and time-consuming reconciliations. Blockchain technology streamlines these operations by creating a decentralized, transparent ledger that all parties can access in real time. This process eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces the risk of errors, and expedites transaction processes.
Blockchain offers self-executing smart contracts with predefined rules to automate supply chain operations. These contracts enable automatic compliance verification, facilitate seamless payment settlements, and trigger actions based on predefined conditions.
For instance, when a shipment reaches a specific location, payment can be triggered automatically, reducing delays and administrative overhead.
2. Reduced risk
The risks associated with the supply chain mainly originate from 4 channels - sourcing, transportation, processing, and distribution. With blockchain, businesses can track and verify every step of the supply chain process, from sourcing to distribution, in a secure and decentralized manner.
This transparency helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, such as counterfeit products, unauthorized modifications, or delays in transportation.
By recording transactions on a distributed ledger, blockchain ensures that all participants have access to the same information, eliminating information discrepancy and reducing the risk of fraud. The immutability of blockchain data prevents tampering or unauthorized changes, providing a reliable and auditable record of every transaction.
3. Enhanced trust
A supply chain typically consists of multiple stakeholders, processes, and transactions. Trust is critical for establishing efficient operations and a sustainable delivery stream. Traditional supply chains often suffer from information disparity, where participants have limited visibility into the activities and transactions of others, leading to inefficiencies and potential fraud.
With blockchain, each transaction is time-stamped and linked to previous transactions, creating an immutable audit trail that can be verified by all parties involved. By having a shared and tamper-proof record of transactions, blockchain technology enables increased trust among supply chain participants.
4. Improved collaboration
A traditional supply chain involves multiple parties, such as manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, retailers, and customers, each with its own systems and databases. This fragmentation often leads to inefficiencies, delays, and a lack of collaboration among the participants. With blockchain, all participants access a shared ledger that records and verifies every transaction or event in real time.
By enabling secure and transparent data sharing, blockchain facilitates better stakeholder coordination and communication. This collaboration allows effective tracking of goods, efficient inventory management, and demand forecasting, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Challenges in implementing blockchain for supply chain management
While blockchain offers multiple benefits in different industries, there are several challenges and considerations in its implementation for supply chain operations that need to be tackled effectively. The prominent challenges associated with implementing blockchain for supply chain management are as follows:
1. Scalability
Several scalability considerations in implementing blockchain for supply chain operations include high-speed connectivity, processing power, storage capacity, and energy consumption. Traditional blockchains use proof-of-work (PoW), which requires significant computational power and time to validate transactions. This technique can result in slower processing of transactions and limits scalability.
Another scalability challenge is the storage and processing requirements of blockchain data. Each transaction is recorded on every node in the network, leading to a large amount of data storage. As the supply chain grows and more transactions occur, the storage and processing demands increase exponentially. The increase in demand can strain the network's resources and hinder scalability.
Various solutions are being considered to mitigate these challenges, including sharding or layer-two protocols that aim to improve scalability by dividing the network into smaller parts or processing transactions off the main chain. Ultimately, companies must accurately forecast their network usage and requirements to deploy the most efficient blockchain solution for their specific supply chain needs.
2. Regulatory compliance
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology raises concerns regarding legal compliance. Different countries and regions have varying regulations and standards for data protection, intellectual property rights, and cross-border transactions. Implementing blockchain in a supply chain requires careful consideration of these regulations to ensure compliance.
One key aspect is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which governs the collection, storage, and personal data processing. Blockchain's immutability and transparency can conflict with GDPR's data protection principles.
Organizations must find ways to reconcile these requirements, such as implementing privacy-enhancing techniques like zero-knowledge proofs or off-chain storage of sensitive data.
Collaboration between blockchain developers, supply chain stakeholders, and regulatory bodies is crucial to address these challenges. Establishing industry standards and guidelines for blockchain implementation can help navigate the complex regulatory landscape and ensure compliance.
Additionally, compliance with import/export regulations, trade sanctions, and product certifications must be integrated into the blockchain system to ensure transparency.
3. Interoperability
As blockchain adoption becomes more mainstream, there must be a universal agreement on interoperability standards for ensuring global alignment. Each blockchain network may have its unique structure, consensus mechanism, and smart contract language, making it difficult to establish a standard protocol for data exchange. Additionally, the scalability and performance of blockchain networks can vary, further complicating interoperability efforts.
There must be universal consensus and interoperable standards to ensure compatibility across multiple blockchain platforms, applications, and ecosystems. This consensus will streamline cross-communication and verify end-to-end operations across the supply chain networks.
Currently, some workarounds in the form of bridges use a combination of “off-chain” relayers and smart contracts. However, this solution has some drawbacks, like high costs and resource-intensive computations. Industry-wide collaboration and standardization efforts are necessary to address these challenges.
Organizations should work together to develop common standards, protocols, and data formats that enable seamless integration and interoperability among different blockchain systems.
4. Industry adoption
Industry adoption is a significant challenge in implementing blockchain for supply chain management. While the technology holds immense promise, its adoption across industries must be balanced. The reluctance to embrace blockchain can be attributed to various factors, including the perceived complexity of the technology, concerns about integration with existing systems, and a lack of understanding of its potential benefits.
Universal industry adoption requires buy-in from various stakeholders within the industry, including manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, retailers, and regulatory bodies. Implementing blockchain requires these parties to align their operations and share data transparently and securely.
This level of cooperation can be difficult to achieve, especially when there is a lack of trust or conflicting interests among the stakeholders.
Industry-wide education and awareness programs are crucial to overcome these challenges. Demonstrating the potential benefits of blockchain, addressing concerns, and showcasing successful use cases can help build confidence and encourage adoption.
Wrapping up
Integrating blockchain technology in supply chain management can transform how businesses operate. From enabling real-time tracking of goods to reducing fraud, blockchain for supply chains streamlines processes, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
Blockchain also enhances collaboration among supply chain stakeholders, fostering a more sustainable and ethical supply chain. Though there are still challenges in its adoption, such as scalability and regulatory frameworks, a willingness to work together and adopt a common framework can provide an effective solution.
Turing’s blockchain development services offer comprehensive solutions - from consulting and smart contracts to end-to-end blockchain integration, ensuring you get a custom solution for your supply chain needs. Our blockchain expertise and innovative approach deliver an ideal solution framework to tackle challenges effectively and drive your business forward at scale.
Talk to an expert today!
Want to accelerate your business with AI?
Talk to one of our solutions architects and get a complimentary GenAI advisory session.
Get Started
Author
Huzefa Chawre
Huzefa is a technical content writer at Turing. He is a computer science graduate and an Oracle-certified associate in Database Administration. Beyond that, he loves sports and is a big football, cricket, and F1 aficionado.
