ETL
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is ETL?
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load. It is a process commonly used in data integration and data warehousing to collect, transform, and load data from various sources into a target system, such as a database, data warehouse, or data lake. The process plays a vital role in data integration and analytics, as it enables organizations to combine and consolidate data from disparate sources into a unified and consistent format.
This unified data can then be used for reporting, business intelligence, data analysis, and decision-making purposes. ETL processes are often automated using specialized tools or programming languages to handle large volumes of data efficiently.
2. Explain what the ETL testing operations include.
- ETL testing operations involve validating and verifying the extraction, transformation, and loading of data in an system. It includes tasks such as data validation, verifying data transformations, assessing data quality, performance testing, error handling testing, data reconciliation, and metadata validation.
- Data validation ensures the accuracy and completeness of extracted data. Transformation verification checks if data has been correctly transformed according to defined rules.
- Data quality assessment ensures data integrity, consistency, and adherence to standards.
- Performance testing evaluates system speed and efficiency under various conditions.
3. Explain the concept of ETL.
Here's a breakdown of each step in the ETL process:
Extract: In this step, data is extracted from multiple heterogeneous sources, which can include databases, spreadsheets, APIs, log files, and more. The data is typically gathered from different systems, formats, or locations.
Transform: Once the data is extracted, it undergoes a series of transformations to clean, normalize, validate, and restructure it into a consistent format suitable for analysis or storage. This step involves applying various business rules, data validation, data cleansing, data enrichment, and aggregation operations to ensure data quality and integrity.
Load: After the data has been transformed, it is loaded into the target system, such as a data warehouse, where it can be stored, queried, and analyzed. The loading process involves writing the transformed data into the appropriate tables or data structures within the target system.
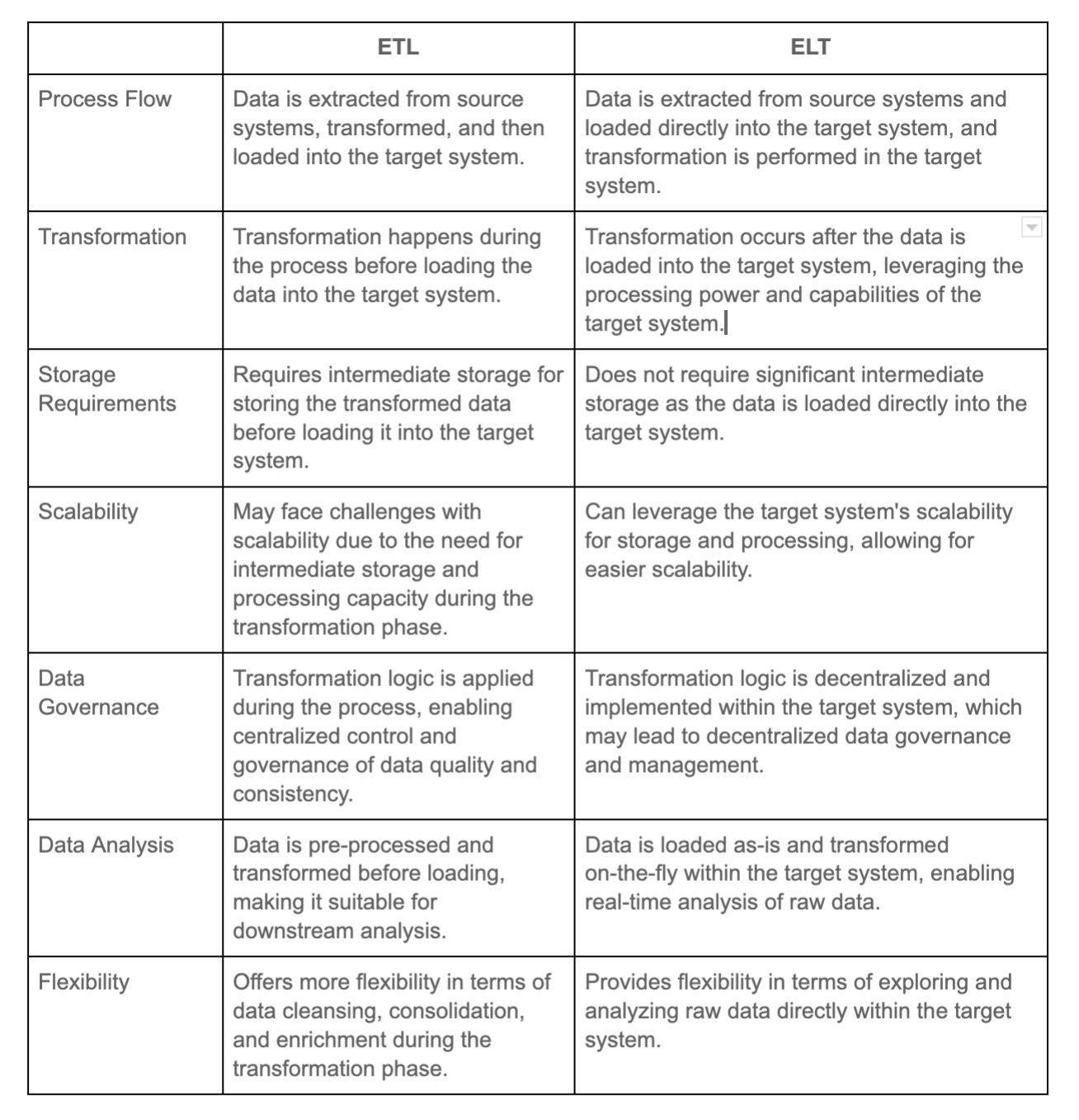
4. Compare between ETL and ELT.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) are two distinct approaches to data integration and processing, each with its own advantages and use cases.
5. What is an ETL process?
The ETL process is typically performed on a scheduled basis to ensure the timely availability of updated data for analysis. It is often used in business intelligence, data analytics, and reporting scenarios where data from multiple sources need to be consolidated, integrated, and made available for analysis.
6. How does ETL process ensure data quality and consistency in the target data warehouse?
The ETL process ensures data quality and consistency in the target data warehouse through several mechanisms.
Data Validation: ETL tools perform data validation checks to ensure that data conforms to specified rules and constraints.
Data Cleansing: ETL tools remove any anomalies or errors in the data through techniques like data standardization and duplicate removal.
Data Transformation: ETL tools transform data into a consistent format, ensuring compatibility with the target data warehouse schema.
Data Profiling: ETL tools analyze the source data to identify data quality issues and provide insights for data cleansing and transformation.
7. How does ETL process work in the context of data integration?
Firstly, data is extracted from various sources like databases, files, and APIs. Then, it undergoes transformation to be cleaned, filtered, and standardized. Lastly, the transformed data is loaded into the target system, like a data warehouse or data lake. ETL ensures data consistency, quality, and accessibility across diverse sources, enabling businesses to make better decisions based on integrated and reliable data.
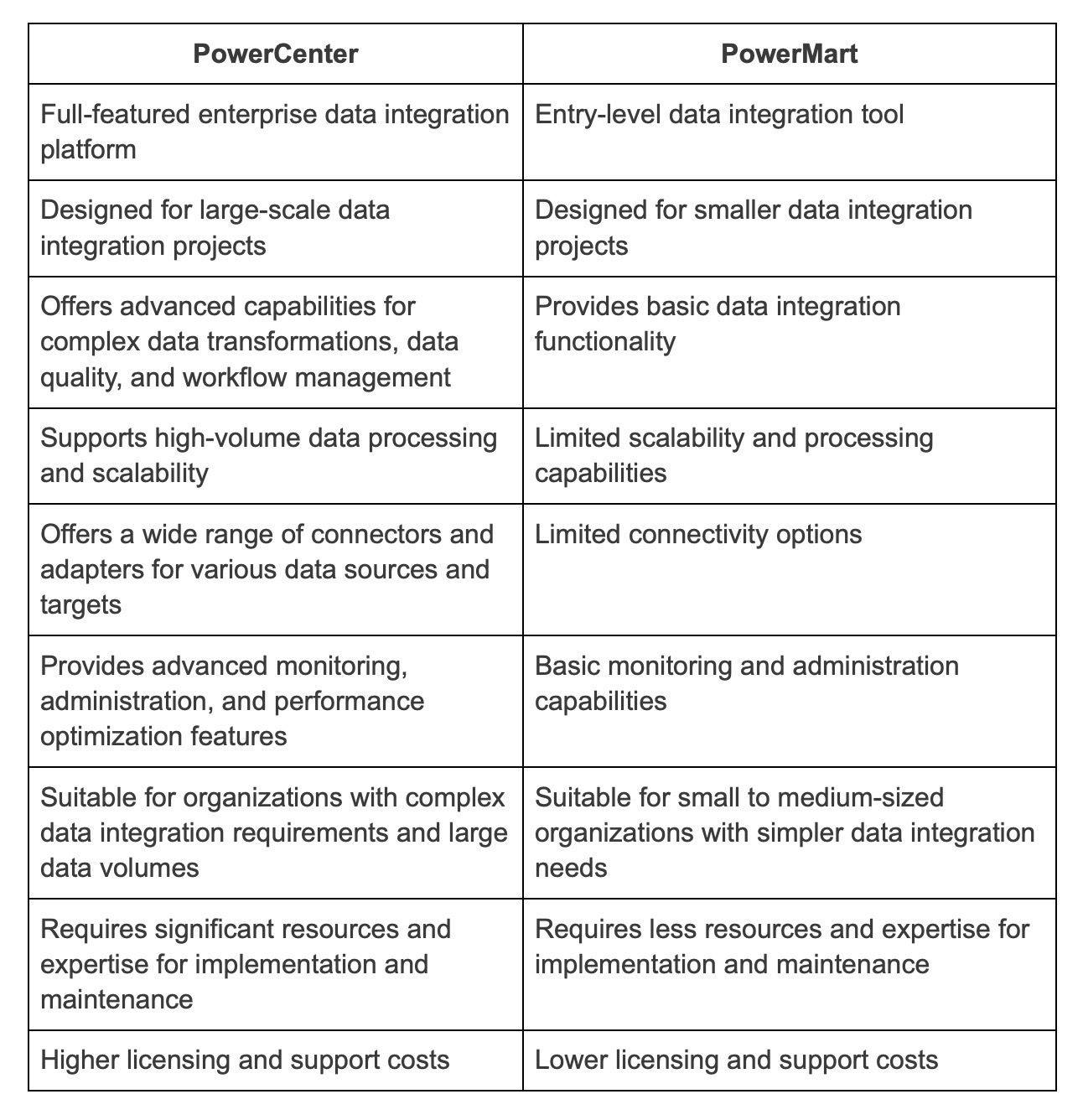
8. With which apps can PowerCenter be connected?
PowerCenter can be connected to various applications through its client tools. Some of the apps that PowerCenter can connect to include:
Informatica Developer: This is a client tool that allows developers to design and develop Data Integration processes using PowerCenter.
Informatica PowerExchange: PowerExchange is an application that provides connectivity to different data sources and targets, allowing PowerCenter to extract, transform, and load data from various systems.
Informatica Cloud: PowerCenter can also integrate with Informatica Cloud, which provides cloud-based data integration and management solutions.
Salesforce: PowerCenter can connect to Salesforce, a popular customer relationship management (CRM) platform, to extract, transform, and load data between Salesforce and other systems.
9. Which partition is used to improve the performance of ETL transactions?
The partition used to improve the performance of ETL transactions is called a "data partition". Data partitioning involves dividing a large dataset into smaller, more manageable partitions. Each partition is then processed independently, allowing for parallel processing and increasing the overall throughput of ETL transactions.
By distributing the workload across multiple partitions, data partitioning can significantly improve the performance of ETL operations, reducing processing time and enhancing overall efficiency.
10. Does PowerMart provide connections to ERP sources?
PowerMart does not offer connectivity to ERP sources or support session partitioning.
11. What is meant by partitioning in ETL?
Partitioning in ETL refers to the process of dividing data into smaller, more manageable subsets or partitions based on certain criteria. These partitions can be based on a variety of factors such as time intervals, geographic regions, or specific attributes of the data.
12. What exactly is a cube?
The cube is one of the critical components in the data processing. Cubes are data processing units that contain dimensions and fact tables from the data warehouse in their most basic form. It gives clients a multidimensional perspective of data, as well as querying and analytical tools.
The types of cubes are:
- OLAP Cubes:
These are OLAP cubes built by clients, end-users, or third-party applications using the Microsoft® PivotTable® Service to access a data warehouse, relational database, or OLAP cube. - Virtual Cubes:
These are composites of one or more real cubes that don't take up any disc space. They only store the definitions of the referenced source cubes, not their data. They're similar to relational database views. - MOLAP Cubes:
On the Analysis Server computer, MOLAP cubes store data aggregations and a copy of the fact data in a multidimensional format. When some extra storage capacity on the Analysis Server machine is available and the best query performance is desired, this is the ideal option. MOLAP local cubes can be used offline and contain all of the essential data for calculating aggregates.
13. Mention what are the types of data warehouse applications?
There are three main types of data warehouse applications:
Information Processing: These applications involve storing and managing large amounts of data for reporting and analysis purposes. They enable users to access and analyze data to make informed business decisions. Examples include generating sales reports, analyzing customer data, and forecasting demand.
Analytical Processing: These applications focus on complex analysis and data mining. They involve using advanced algorithms and statistical models to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships in data. Examples include identifying market trends, predicting customer behavior, and optimizing supply chain management.
Data Mining: This application involves the process of discovering patterns and relationships in large datasets. It uses various techniques such as clustering, classification, and association to extract valuable insights from the data. Data mining aims to uncover hidden patterns and make predictions or decisions based on them.
14. What are the various tools used in ETL?
Cognos Decision Stream: This is an ETL tool provided by IBM Cognos for data extraction, transformation, and loading. It's designed to work with IBM Cognos BI solutions.
Oracle Warehouse Builder: Oracle's ETL tool for designing, deploying, and managing data integration processes. It's tightly integrated with Oracle databases and offers data quality and data profiling features.
Business Objects XI: While Business Objects is primarily known for its business intelligence solutions, it also offers ETL capabilities through its Data Integrator component. It's used for building and managing ETL processes.
SAS Business Warehouse: SAS provides a suite of business intelligence and analytics tools, including a data warehousing solution for ETL processes. It's used for data integration, transformation, and loading into a data warehouse.
SAS Enterprise ETL Server: Another offering from SAS, this tool focuses on data integration and ETL processes. It's designed to handle complex data transformations and integration scenarios.
15. What are an ETL tester's roles and responsibilities?
You will often come across this ETL testing interview question. ETL testers are in high demand because ETL testing is so crucial. Data sources are validated, data is extracted, transformation logic is applied, and data is loaded into target tables by ETL testers. An ETL tester's primary responsibilities are as follows:
- In-depth understanding of ETL tools and methods.
- Thoroughly test the ETL software.
- Examine the data warehouse testing component.
- Carry out the data-driven backend test.
- Create and execute test cases, test plans, test harnesses, and so on.
- Identifies issues and recommends the best solutions.
- Examine and sign off on the requirements and design specifications.
- Creating SQL queries for testing purposes.
- Various sorts of tests, such as primary keys, defaults, and checks of other ETL-related functions, should be performed.
- Carry out frequent quality inspections.
16. What is fact? What are the types of facts?
A "fact" refers to a piece of information or data that is quantifiable and measurable. Facts are typically numerical data points representing business metrics or performance measures. They are used in combination with dimensions (categorical attributes) to provide valuable insights and analysis in a data warehouse.
There are different types of facts that capture various aspects of business operations:
Additive Facts: These are facts that can be aggregated across all dimensions. Common examples include sales revenue, quantity sold, and profit. Additive facts can be summed up across different dimensions like time, product, and region.
Semi-additive Facts: These are facts that can be aggregated across some dimensions but not all. An example is the "account balance." While you can sum balances across time (months or quarters), you can't sum them across other dimensions like customer.
Non-additive Facts: These are facts that cannot be aggregated at all. They are usually ratios, percentages, or other calculations that lose their meaning when aggregated. Examples include profit margin and average.
Factless Facts: These are facts that have no measurable numeric value but still play a significant role in data analysis. They represent events or occurrences and serve to establish relationships between dimensions.
17. What are initial loads and full loads?
Initial loads and full loads are terms commonly used in data integration or data warehousing. They refer to different processes of loading data into a system:
Initial Load: The initial load is the first process of loading data into a system or database. It typically involves loading a large amount of data from various sources into the target system. This is usually done while setting up a new system or database for the first time.
Full Load: A full load is a process of loading or refreshing all the data in a system or database. It involves completely replacing the existing data with a new set of data.
18. What is meant by incremental load?
Incremental load refers to adding or updating only the new or modified data since the last data load, rather than reloading the entire dataset. It is a method used to efficiently update a data system by only bringing in changes since the last load.
19. What is a 3-tier system in ETL?
A 3-tier system in ETL refers to a modular client-server architecture design for handling data integration processes. The architecture is composed of three logical and physical computing tiers: the presentation tier, the application tier, and the data tier.
The presentation tier, or user interface, is where users view data; the application tier handles logic, and the data tier stores information produced by the ETL process.
20. What are the three tiers in ETL?
The three tiers in ETL are as follows:
- Extraction tier, which involves extracting data from source systems like databases, CRMs, spreadsheets, etc.
- Transformation tier, which involves cleaning, structuring, and transforming raw data so that it can be further analyzed.
- Loading tier, which involves loading the transformed data into a data warehouse, data mart, or other targeted system.
21. What are the various ETL testing challenges that you face on a regular basis?
Despite the necessity of ETL testing, businesses may encounter significant difficulties when attempting to integrate it into their systems. ETL testing is difficult due to the volume of data involved or the diverse nature of the data. Some of these challenges are as follows:
- Changes in client requirements necessitate the re-run of test cases.
- Changing client needs may demand a tester creating/modifying new mapping papers and SQL scripts, which can be a time-consuming and labor-intensive procedure.
- Uncertainty over company requirements or personnel who are unaware of them.
- Data loss may occur during migration, making source-to-destination reconciliation problematic.
- A data source that is incomplete or corrupt.
- Incorporating real-time data may have an influence on reconciliation between data sources and goals.
- Due to the enormous number of historical data, the system may experience memory difficulties.
- Testing with ineffective instruments or in an unstable environment
22. What are the names of the layers in ETL?
The initial stage of the ETL process is known as the source layer, which is where data is initially received. Following that is the integration layer, where transformed data is stored. Finally, the dimension layer represents the ultimate presentation layer.
23. Can there be sub-steps for each of the ETL steps?
Yes, each of the ETL steps can have sub-steps or sub-processes to further refine and enhance the data integration process. These sub-steps can vary depending on the specific requirements and complexities of the data being processed.
24. Explain what transformation is.
Transformation refers to the process of manipulating and altering data from its source format into a format that is suitable for analysis, reporting, and storage. It involves applying various operations and functions to the extracted data to clean, enrich, aggregate, and restructure it according to the requirements of the target system or data warehouse.
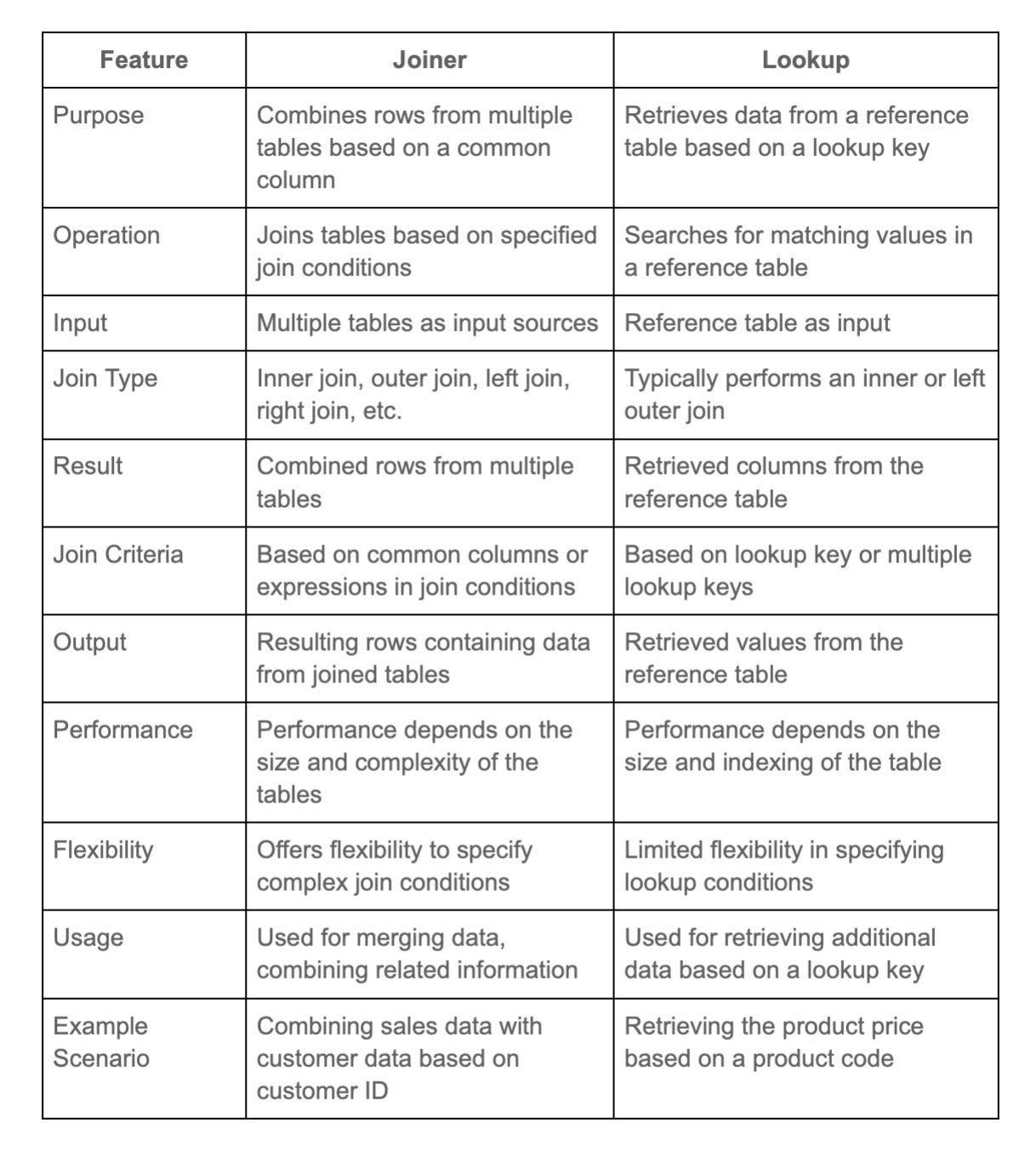
25. Explain the use of Lookup Transformation.
The Lookup Transformation in ETL is used to retrieve and match data from a reference table or dataset based on a key or set of columns. It allows for the enrichment or validation of data during transformation by comparing values to the reference data.
This helps in ensuring data accuracy, and integrity, and in creating relationships between datasets for analysis or reporting purposes.
26. Explain what is partitioning, hash partitioning, and round-robin partitioning.
Partitioning is the process of splitting a large dataset into smaller, more manageable parts for better performance and scalability. Hash partitioning divides data based on a hashing algorithm to distribute rows evenly across partitions. Round-robin partitioning distributes rows evenly by cycling through each partition in a circular fashion.
These partitioning methods help to reduce data processing overhead and optimize data retrieval times for queries or operations involving large datasets.
27. Mention what is the advantage of using a DataReader Destination Adapter.
The advantage of using a DataReader Destination Adapter in ETL is its efficiency and performance. The DataReader Adapter allows for fast and direct loading of data into a target database without the need for additional transformation or processing.
It utilizes a streaming approach, reading data row by row, reducing memory consumption, and providing a high-throughput method for loading large amounts of data efficiently.
28. Using SSIS ( SQL Server Integration Service) what are the possible ways to update tables?
There are several methods available for updating the table using SSIS. These include utilizing a SQL command, employing a staging table, utilizing a cache, utilizing the Script Task, and if MSSQL is being used, using the full database name for updating.
29. In case you have a non-OLEDB (Object Linking and Embedding Database) source for the lookup what would you do?
If the source system for the lookup is non-OLEDB, there are a few options to consider:
- Use a different ETL tool or connector that supports the non-OLEDB source system natively.
- Explore whether the non-OLEDB source system can be accessed through an API or web service, and use an ETL tool that can leverage that API connection to retrieve the lookup data.
- Convert the non-OLEDB data source into a format that can be used by the tool. For example, if the lookup data is in a flat file format, use a file connector or adapter to read the data into the pipeline.
- Use a custom script or code to extract and transform the non-OLEDB source data into a compatible format that can be used by the tool.
- The approach taken will depend on the specific details of the non-OLEDB source system, the availability of connectors or APIs, the capability of the tool, and the level of effort and complexity required to implement the desired solution.
30. In what case do you use dynamic cache and static cache in connected and unconnected transformations?
Dynamic and static cache are caching mechanisms used in ETL transformations to improve performance while performing lookups. The choice between dynamic and static cache in connected transformations depends on the volatility of the lookup source data.
A dynamic cache is used when the lookup source data is subject to modification or updating during the session run, while a static cache is used when the lookup source data is unchanged during session execution. In unconnected transformations, the selection of dynamic or static cache relies on the nature of the lookup and the frequency of updates.
31. Describe the ETL cycle's three-layer design.
Staging layers, data integration layers, and access layers are commonly used in ETL tool-based data warehouses. The architecture is divided into three layers:
- Data retrieved from numerous data sources is stored in a staging layer, also known as a source layer.
- The data integration layer is responsible for transforming data from the staging layer to the database layer.
- Users can get data for analytical reporting and information retrieval via the Access Layer, also known as a dimension layer.
32. Why is ETL testing required?
ETL testing is essential to ensure that data is accurately extracted, transformed, and loaded from source systems into the destination system. The process guarantees that the data is correctly transformed, the data lineage is maintained, data quality is maintained, and that all business rules, data aggregations, and calculations are correctly applied.
33. What is the definition of BI (Business Intelligence)?
Acquiring, cleaning, analyzing, integrating, and sharing data as a method of generating actionable insights and boosting corporate success is what Business Intelligence (BI) is all about. An efficient BI test evaluates staging data, the ETL process, and BI reports, as well as ensures that the implementation is trustworthy. In simple terms, business intelligence (BI) is a technique for gathering raw business data and transforming it into actionable information for a company. The correctness and legitimacy of insights from the BI process are evaluated by BI Testing.
34. What role does data cleaning play?
Data cleaning is also known as data cleansing or data scrubbing. This is the process of deleting data from a dataset that is missing, duplicated, corrupted, or wrong. The importance of data cleaning grows when the necessity to combine multiple data sources becomes more evident, such as in data warehouses or federated database systems. Because the particular phases in a data cleaning process differ based on the dataset, creating a template for your process will help you accomplish it correctly and consistently.
35. What are Dimensions?
Dimensions in ETL refer to the specific attributes or characteristics used to categorize and provide context to data in a data warehouse. They play a crucial role in organizing and understanding the data.
Key features of dimensions include:
Descriptive attributes: Dimensions provide descriptive information about the data, such as product name, customer location, or time period.
Hierarchical relationship: Dimensions can be arranged hierarchically, allowing for drill-down analysis. For example, a product dimension may have levels like category, subcategory, and product.
Referenceable: Dimensions can be referenced by fact tables using a foreign key relationship, enabling efficient querying and joining with other data.
Wrapping up
The list of ETL interview questions and answers provided here will help you prepare for your ETL interview. These ETL interview questions can aid you in resolving or producing similar queries.
However, these data warehouse interview questions for ETL developer would not be the only focus of an ETL interview. Knowing how a person fares in difficult circumstances and how a person behaves among his peers can give the recruiters important insights about the candidate.
Collaborate with Turing if you're a recruiter looking to hire ETL developers from the top 1%. If you're an experienced ETL developer searching for a new opportunity, Turing is a great place to start.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber ETL developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.