100+ essential full-stack developer interview questions and answers for 2024
Hire Full Stack developers
Full Stack
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is full-stack development? What are the skills needed for a full-stack developer?
Full stack development is the comprehensive development (front-end & back-end) process of applications or websites. The full-stack developers are responsible for developing the front end, which is the presentation layer, and the back end, which consists of business logic and the database layer.
A full-stack developer needs to have a wide range of skills, including front-end languages & frameworks, back-end languages, and server-side technologies, plus knowledge of other productivity tools.
2. As a Full-stack developer, list down your favorite technologies that you like to leverage and tell us why they are your favorites.
This full-stack developer interview question aims to gauge your knowledge and how well-versed you are with different types of technologies. When you answer, make sure you add your personal experience linked with the particular language/languages. In a full-stack developer interview, talking about your projects will help you a lot.
The following is what a full-stack developer must introduce:
- Programming Languages: A full-stack developer must be fluent in many programming languages, such as Java, Python, Ruby, C++, and others. Based on the programming language, one must be familiar with various approaches to plan, develop, implement, and test the project.
- Front-end: Knowledge of front-end technologies such as HTML5, CSS3, Angular, and others is required. Understanding third-party libraries like jQuery provide additional benefits.
- Frameworks: Proficiency with development frameworks such as Spring, Spring Boot, MyBatis, Django, Hibernate and others.
- Databases: You should have an idea regarding at least one database. It is enough if you are familiar with either MySQL, Oracle, or MongoDB.
- Design Ability: Hands-on experience in popular design skills, such as UI and UX design, is also required.
3. Talk about MVC and MVP. Are they similar to each other?
Model View Controller (MVC)
MVC is an architectural paradigm for creating Java Enterprise Applications. It divides a program into three logical parts: Model, View, and Controller. It isolates the display layer (View component) from the business-specific logic (Model component).
Data and logic relating to it are contained in the model components. Model objects are shown within the user interface using the View component. The Controller accepts the input and invokes model objects based on the handler mapping. It also transfers model objects to views to show output within the view layer.
Model View Presenter (MVP)
Model View Presenter is an acronym for Model View Presenter. The MVC architectural pattern inspired it. It adds an extra layer to the architectural pattern (known as indirection) that divides the View and Controller into View and Presenter. A Presenter takes the position of the Controller. In MVC, it's on the same level as View. It includes the View's UI business logic. The Presenter receives the invocations straight from the View. It keeps the action (events) going between the View and the Model. The View is not directly communicated with by the Presenter. It connects with the user via a user interface.
No, MVC and MVP are not similar at all. The most significant difference between MVC and MVP architectural patterns is that with MVC, the data from the Model is not sent to the View via the Controller. It simply instructs the View to obtain data from the Model.
The View and Model layers are linked together in the MVP architectural design. The data from the Model is received by the presenter, who then transmits it to the View to display.
Another distinction is that MVC is more commonly used in web frameworks, whereas MVP is more commonly used in app development.
4. What is load time?
The average time it takes for a page to load on your screen is called page load time. It's computed from the beginning (when you click on a page link or write in a Web address) to the end (when the page is fully loaded in the browser).
5. Explain two-phases commit (2PC) in the database.
When an error circumstance occurs, a two-phase commit (2PC) is a feature of transaction processing systems that allows databases to restore to their pre-transaction state. The two-phase commit technique ensures that either all of the databases are updated, or none of them are updated. As a consequence, the databases are kept in sync.
6. How is a blue/green deployment different from a rolling deployment? Explain.
In Blue/Green Deployment, you have two complete ecosystems. The Blue environment is now operational, whereas the Green environment is the one you want to upgrade to. When you change the environment from blue to green, the traffic is redirected to your new green environment. You can delete or save your old blue environment as a backup until the green environment is formed.
In Rolling Deployment, there is only one complete environment. Before being relocated to another subset, the code is deployed in a subset of the same environment's instances.
7. List down the various disadvantages of GraphQL.
- You must transmit the queries from the client; you may send strings if you want greater convenience and caching, but you need to use a client library.
- You must define the schema ahead of time, therefore more effort is required before seeing any results.
- You must have a GraphQL endpoint on your server, which is more new libraries that you may not be familiar with.
- Graphql queries take up more space than visiting a REST API.
- The server must perform additional processing to parse the query and check the arguments.
8. Explain whether null and undefined are similar in JavaScript or not.
No, null is not at all similar to undefined in JavaScript.
Null: A null value has been assigned to a variable. When used with the typeof operator, the result is an object. Because the programmer uses null to represent a variable with no value, we should never set a variable to null. It's worth noting that JavaScript will never set the value to null by default.
Undefined: When a variable is declared but not given a value, it is considered undefined. It is possible that a variable doesn't exist at all. When used with the typeof operator, the outcome is undefined. In JSON, it isn't valid.
9. What do you understand by MEAN Stack?
MEAN stack is a user-friendly free and open-source JavaScript framework for creating dynamic web pages and online apps. The MEAN stack has the advantage of running only one language, JavaScript, on all application layers, making it more efficient.
MEAN stack comprises the following:
Database: MongoDB
Web Framework: Express.js
Frontend Framework: AngularJS
Server Platform: Node.js
10. Mention the different ways how to avoid deadlock in Java.
Deadlock occurs when two or more threads attempt to access the same resources simultaneously in Java. These threads will eventually be unable to access the resource and will remain to wait indefinitely.
There are several ways to avoid deadlock. Some of them are:
By Avoiding Unnecessary Locks: We should only use locks on members who need them. Locks are used unnecessarily, resulting in a stalemate. It is suggested that you utilize a data structure that is not locked. Keep your code as lock-free as possible. Instead of utilizing a synchronized ArrayList, consider using a ConcurrentLinkedQueue.
By Avoiding Nested Locks: Another technique to avoid deadlock is to provide a lock to many threads if one thread has already been given a lock. We can't assign a lock to many threads because of this.
By Using the Thread.join() method: We can have a deadlock if two threads wait eternally for each other to finish. It's usually advisable to use join with the maximum time you want to wait for the thread to finish if a thread has to wait for another thread to finish.
Utilize Lock Ordering: Each lock should have a number value assigned to it. Obtain the locks with a lower numeric value before acquiring the locks with a higher numeric value.
Lock Time-out: We may also specify how long it takes for a thread to get a lock. If a thread fails to obtain a lock, it must wait a certain amount of time before attempting to acquire a lock again.
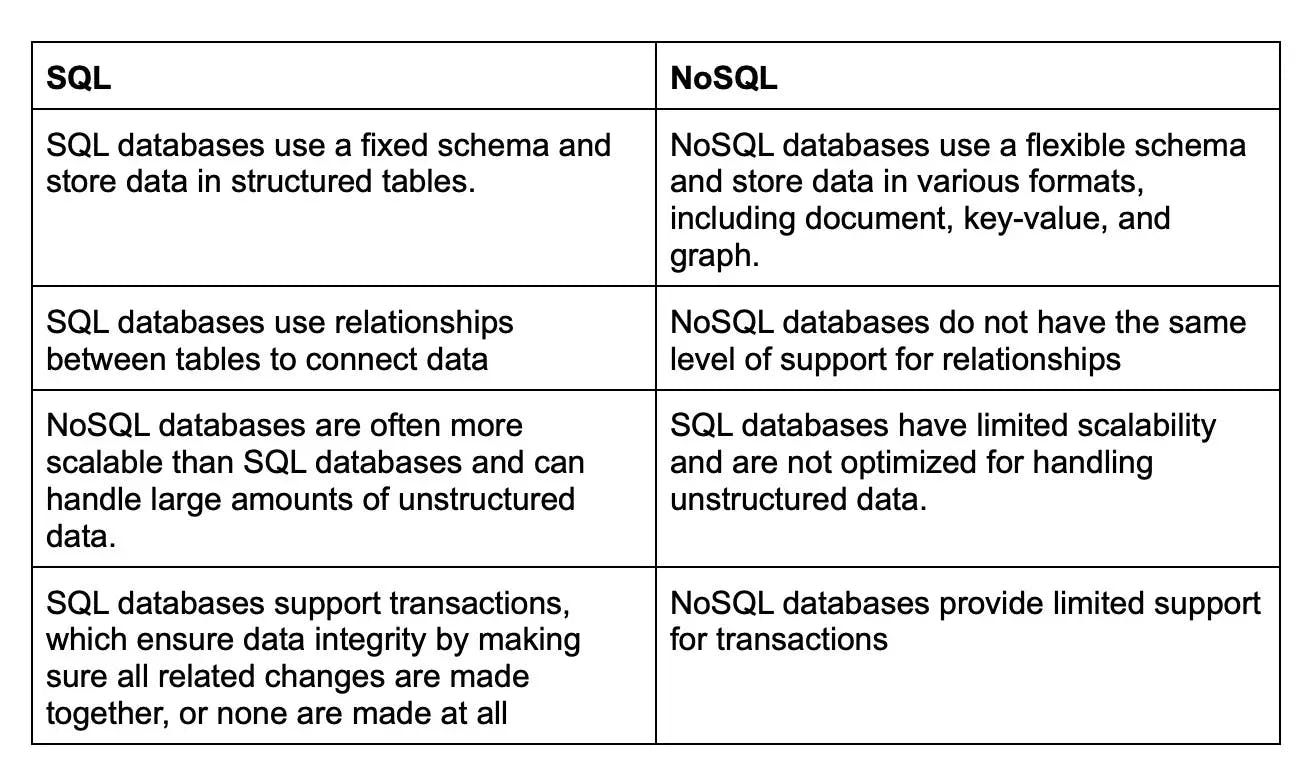
11. What are the main differences between a relational and a NoSQL database?
Relational databases organize data into tables with predefined schema, supporting complex queries using SQL. NoSQL databases use a flexible schema or are schema-less, providing more scalability and faster data access but with simpler and less ACID-compliant querying.
12. What front-end technologies should a full-stack developer be proficient with?
A full-stack developer should be proficient in many front-end technologies:
Front-end languages: HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Front-end frameworks: AngularJS, VueJS, Bootstrap, Next.js, among others frontend frameworks
13. What back-end technologies should a full-stack developer be skilled in?
Full-stack developers should be skilled in various back-end technologies like Python, Java, Ruby, PHP, ASP.NET, Oracle, MySQL, MongoDB, and others.
14. Which are the tools used by full-stack developers?
Typescript, Webstorm, Github, Visual studio code, Electron, Slack, and Backbone are some popular tools full-stack developers use.
15. What is continuous integration?
Continuous integration (CI) is an important aspect of full-stack software development. It ensures that changes to a codebase are tested and integrated regularly into the shared repository system, avoiding unforeseen bugs and ensuring smooth deployment of applications.
Ultimately, CI enables rapid development cycles, frequent feedback loops between team members, and faster releases with fewer defects.
16. What is CORS?
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a security feature that allows or denies web pages from making requests to a server with a different origin (domain, protocol, or port). It's crucial because it enables control over which origins can access server resources, preventing unauthorized cross-origin requests.
17. Explain pair programming in brief.
Pair programming is a software development method where two developers work together at one workstation to solve problems. One developer writes code, while the other provides feedback and helps in the improvement. This method allows developers to use their strengths and collaborate to complete tasks more efficiently.
18. What is multithreading?
Multithreading is a process in which multiple threads are executed concurrently within the same program. Multithreading is commonly used in multitasking programs like web browsers and gaming engines.
With modern CPUs with multiple cores, multithreading has become increasingly popular as an efficient way to optimize the utilization of all cores in a processor.
19. What do you mean by dependency injection?
Dependency Injection (DI) in full-stack development is a software design pattern that enables developers to inject code into an application without the need for tight coupling or direct referencing. It enables developers to easily swap out one piece of code for another when needed, making it an essential part of modern web development.
20. Explain Inversion of Control.
Inversion of Control is a design principle where classes are loosely coupled for easy maintenance and flexibility. Instead of a module or class controlling the flow of execution and managing the dependencies of its collaborators, IoC delegation of responsibility is to an external entity, typically an IoC container or framework.
By doing so, IoC promotes loose coupling between modules and classes, which can make the code more flexible, extensible, and maintainable.
21. What are the fundamental design patterns in full-stack development?
The primary design patterns in full-stack development are MVC, Microservices, and Single page applications, among others.
Model-View-Controller (MVC): This pattern separates an application into three interconnected components: the model (data), the view (user interface), and the controller (logic).
Microservices: This pattern involves breaking an application into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Single Page Application (SPA): SPA is a web application that loads a single HTML page, dynamically updating the content as the user interacts with it, providing a fluid user experience similar to a desktop or mobile app. SPAs typically use AJAX and frameworks like Angular, React, or Vue.
22. What is the difference between GraphQL and REST?
GraphQL and REST are two popular API design options for creating web services. GraphQL is a query language for APIs that provides an alternative to REST, which uses URL paths and request methods to perform actions.
GraphQL allows for more precise querying by providing a type system and allowing clients to ask for only the fields they need in a single request.
23. How would you reduce the load time and improve a website's performance?
Here are some methods to help reduce load time and improve a website’s performance:
- Browser caching
- Image compression & file optimization
- Reduce HTTP requests
- Moving stylesheet references to the top of the page
- Removal of unused scripts and files
- Utilization of content delivery network (CDN)
24. What is polling? What are its types?
Polling is a client-side technique where a client sends requests to a server at regular intervals to check if there are any updates or new information available. The server responds to each request with the latest information, even if there have been no changes since the previous request.
This can be useful in situations where real-time updates are not critical, and a client does not want to refresh the page constantly. However, polling can be both inefficient and put strain on the server unnecessarily if requests are made too frequently. The two different types of polling are Long polling and Short polling.
25. What are the main differences between REST and GraphQL APIs?
REST APIs use predefined routes for data access, typically require multiple calls to access related data, and may over-fetch or under-fetch data. GraphQL APIs use a single endpoint, allowing clients to request the data they need and their exact shape, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues.
26. What is long polling and short polling?
Long polling is a computer networking method where a request for information is kept open until new data comes in or the request times out. It is a technique used in web development where the client sends a request to the server, but instead of immediately responding with any available data, the server keeps the request open until new data becomes available or a timeout period elapses. This can be useful for real-time applications where immediate updates are needed without constantly sending requests to the server.
Short polling is a technique used to send client requests at regular intervals. In short polling, the client sends requests to the server at regular intervals, regardless of whether there is new data available on the server or not. If there is no new data, the server simply responds with a null or empty response. This approach can result in unnecessary network traffic and consume more resources than other techniques, such as long polling or server-sent events.
27. Explain event delegation in JavaScript.
Event delegation is a technique in which you add an event listener to a parent element instead of adding individual listeners to each child element. This takes advantage of event bubbling, where events propagate up through the DOM tree. Event delegation is useful because it reduces the number of event listeners, improving performance and keeping the code cleaner.
28. Can you explain what middleware is in the context of backend development?
Middleware is a layer in the application processing flow that can handle requests and responses between the client and server. Middleware typically includes functions for authentication, validation, logging, error handling, or modifying request and response objects.
29. Explain normalization and denormalization.
Normalization refers to the process of data separation into multiple tables to reduce data redundancy. It involves dividing a database into two or more tables and defining relationships between them.
The main goal of normalization is to eliminate data duplication and ensure that each piece of data is stored in only one place, which reduces the risk of data inconsistencies and anomalies.
De-normalization refers to consolidating data from multiple tables into a single table for easy access and retrieval. It is usually implemented on a database that is previously normalized for optimizing performance.
De-normalization can improve performance for read-heavy workloads, but it can also make data updates more complex and increase the risk of data inconsistencies.
30. What is the difference between normalization and resetting CSS?
Normalize.css is a CSS file that renders consistency across elements as the default styling. The CSS reset is used to eliminate all the existing built-in styling options.
31. What are responsive design and adaptive design in web development?
Responsive design is an approach where a website's layout and design adjust fluidly based on the user's screen size and resolution. Adaptive design is an approach where the server delivers different designs or layouts depending on the device in use, usually based on a set of predefined screen sizes or breakpoints.
32. How do you identify a memory leak?
You can identify a memory leak using methods such as memory profilers, verbose garbage collection, and heap dumps.
Memory Profilers: These tools can help you identify memory leaks by showing you how much each object in your program uses memory.
Garbage Collection: Most modern programming languages use garbage collection to automatically free up memory that is no longer being used by your program
Heap Dumps: A heap dump is a snapshot of the memory usage in your program at a particular point in time. Analyzing the heap dump lets you see which objects take up the most memory and potentially identify memory leaks.
33. What are the top tools used to test the code's functionality?
Several tools for testing code functionality are widely used across different programming languages and environments. Some popular testing tools include:
JUnit: A widely-used testing framework for Java applications, JUnit provides support for assertions, test runners, and test suites.
Mocha: A feature-rich JavaScript testing framework for Node.js and browser-based applications, Mocha offers support for asynchronous testing, test coverage reports, and plugin integrations.
Jest: A JavaScript testing framework developed by Facebook, Jest is commonly used for testing React applications and provides built-in support for mocking, coverage reporting, and parallel test execution.
Karma: A test runner used in tandem with other testing libraries like Jasmine or Mocha, Karma enables testing of JavaScript code across real browsers and devices.
Jasmine: A behavior-driven development (BDD) framework for JavaScript, Jasmine is used both for frontend and Node.js environments and features an intuitive syntax, spies, and custom matcher support.
Selenium: A widely-used browser automation tool, Selenium supports multiple programming languages and allows for end-to-end testing of web applications, simulating real user interactions.
Cypress: A JavaScript-based end-to-end testing framework, Cypress enables fast and efficient testing of web applications running in modern browsers, featuring real-time reloading and automatic waiting.
34. What is an observer pattern?
The Observer pattern is a behavioral design pattern used in software development, including full stack development, to establish a one-to-many relationship between objects. In this pattern, an object (called the subject) maintains a list of its dependents (called observers), which need to be updated when the subject's state changes. This approach promotes loose coupling between the subject and the observers, enabling better scalability and easier modification of the system.
35. What is JWT (JSON Web Token) and how is it used for authentication?
JWT is a compact, URL-safe, JSON-based method for securely transmitting information between parties. JWTs can be signed and/or encrypted. They're commonly used for authentication, where a server generates a token upon successful user login, and the client includes the token in subsequent requests to validate the user's identity and authorization.
36. What are GET and POST methods used for?
Both GET and POST are HTTP methods used to request data from and send data to a server. They have different purposes and use cases:
GET
- The GET method is used to request data from a specified resource (identified by a URI).
- It is typically used to fetch data or a webpage from a server without making any changes to the resources on the server.
- GET requests can be cached by the browser, and their history is saved in browser history.
- Because GET requests send data as URL parameters, they have length restrictions and are less secure, making them unsuitable for passing sensitive information.
- GET requests should be idempotent, meaning that making the same request multiple times should have the same effect as making it once.
POST
- The POST method sends data to the server to create or update a resource.
- It is used to send large amounts of data or sensitive information to the server, as the data is sent within the request's body, hidden from the URL.
- POST requests are not cached by the browser and don't show in browser history.
- Since POST requests can potentially have side effects (e.g., creating or modifying resources), they should not be idempotent.
- POST is often used in combination with forms to submit user input data, create a new record in a database, or upload files.
In summary, GET requests are used to fetch data without modifying server-side resources, while POST requests are used to send data to create or update resources on the server.
37. Explain the Callback function in JavaScript?
The Callback function in JavaScript is used as an argument referencing a different function. The callback function is typically used to handle events, perform asynchronous tasks, or respond to user input.
When the function that receives the callback is executed, it calls the callback function to perform some action or return a value. The callback function can be a predefined function or a function defined on the fly.
38. What is a data attribute?
A data attribute is a descriptor for a specific object or a data point. In programming, data attributes are used to store data values and information within an object or a variable. For example, if you have an object representing a car, its data attributes might include its make, model, year, color, etc.
39. What is the difference between client-side scripting and server-side scripting?
Client-side scripting involves writing the code and programming for the front end - the module with which the users directly interact. The server-side scripting is related to programming for the back-end - the module not directly seen by the users.
Wrapping up
So, this was a comprehensive list of the latest 100 interview questions related to full-stack development. If you are looking to apply for top remote full-stack jobs, these questions can provide a quick overview of the broad concepts for your full-stack developer job interview.
Beyond this, it is recommended that you work on your practical and soft skills and be prepared to answer questions associated with teamwork, communication, leadership, and collaboration.
If you are a hiring manager, these technical questions provide a template to test the candidate on the different aspects of full-stack development. If you want to simplify your hiring process and significantly reduce the hiring time, then you can sign up on Turing. Our AI-powered talent cloud vets the remote developers on 100+ skills, 15+ roles, and 7+ seniority levels. Get in touch now.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber Full Stack developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.