MySQL
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is MySQL clustering?
MySQL clustering, also known as MySQL Cluster or MySQL NDB Cluster, is a high-availability, scalable, and distributed database architecture that ensures fault tolerance and automatic data partitioning across multiple nodes. It combines the MySQL server with the NDB (Network DataBase) storage engine and provides real-time, in-memory storage with support for disk-based data as well.
The main components of MySQL Cluster are:
Data Nodes (NDB storage engine): These store the actual data in a partitioned and replicated manner, ensuring data availability and redundancy. Each data node operates in parallel, which improves performance and resilience.
MySQL Server Nodes (SQL Nodes): These are conventional MySQL servers that connect to the data nodes, processing SQL queries and transactions for client applications.
Management Nodes: These nodes handle the configuration and orchestration of the cluster, monitoring its health and managing node membership.
2. What is the purpose of the SELECT statement in MySQL?
The SELECT statement is used to retrieve data from one or more tables in a MySQL database. It's a fundamental SQL command and allows specifying various clauses like WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, and HAVING to define which data should be returned and how it should be organized.
3. What is normalization?
Normalization is the process of organizing a relational database's structure to reduce data redundancy, improve data integrity, and optimize its performance. The primary goal of normalization is to eliminate anomalies in the data and create a better database design by dividing large tables into smaller, related ones and defining relationships between them.
Normalization involves organizing data into multiple tables, ensuring that each table serves a single purpose and contains minimal redundant data. The process is carried out through a series of normalization forms called normal forms, including First Normal Form (1NF), Second Normal Form (2NF), Third Normal Form (3NF), Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF), Fourth Normal Form (4NF), and Fifth Normal Form (5NF). Each normal form has specific rules and builds on the previous one, leading to a more organized and efficient database structure.
4. What are the different data types in MySQL?
MySQL offers various data types to store different types of information. These data types are broadly categorized into the following groups:
Numeric Data Types:
INT: A standard integer, signed range (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) or unsigned range (0 to 4,294,967,295).
FLOAT: A floating-point number with single-precision (approximate values).
DECIMAL: A fixed-point, exact-number data type for storing precise values (such as monetary amounts).
Date and Time Data Types:
DATE: Stores a date in the format 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
TIME: Stores a time in the format 'hh:mm:ss'.
String Data Types:
CHAR: A fixed-length string, with a specified maximum length between 1 and 255 characters.
VARCHAR: A variable-length string, with a specified maximum length between 1 and 65,535 characters.
Spatial Data Types: Spatial data types are used for storing geometric and geographic objects, such as points, lines, and polygons.
5. What is the difference between MySQL and SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standardized programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases. It provides a consistent syntax and set of commands for creating, querying, updating, and deleting data stored in relational databases. SQL is not tied to any specific vendor or database system; instead, it serves as the foundation for working with various database management systems.
MySQL, on the other hand, is an open-source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) that uses SQL to interact with the data stored in its databases. Developed by Oracle Corporation, MySQL is one of the most popular RDBMS solutions due to its speed, reliability, and ease of use. MySQL supports many database features, such as transactions, indexing, and stored procedures.
Note: Also read - SQL vs NoSQL Database
6. How can you install MySQL on your system?
To install MySQL on your system, follow the steps for the specific operating system you are using:
For Windows:
- Download the MySQL Community Edition installer for Windows from the official MySQL website: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
- Run the installer and choose the "Setup Type" according to your requirements. Common options are "Server only," "Full," and "Custom."
- Follow the installation wizard, and configure the MySQL server according to your preferences.
- Complete the installation process, making sure to set your MySQL root password and any other user credentials needed.
- MySQL service should start running automatically after installation. You can manage it using the MySQL Workbench or the command line.
For macOS:
- Download the MySQL Community Edition installer for macOS from the official MySQL website: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/
- Open the downloaded .dmg file and follow the installation instructions.
- During installation, ensure to note the root password as it will be required to connect to your MySQL server.
- After completing the installation, you can manage MySQL server using the MySQL Workbench, the command line, or macOS preferences.
For Linux (using APT on Debian/Ubuntu):
- Update package information and install the MySQL APT repository
- Install MySQL server and client packages
- During the installation process, you will be prompted to set a password for the MySQL root user.
- To manage the MySQL server, use the command line or install MySQL Workbench.
After installing MySQL, you can connect to the MySQL server using various client tools like the command-line client (mysql), MySQL Workbench, or any other graphical tools of your preference.
7. How can you start and stop the MySQL server?
To start and stop the MySQL server, you can use the appropriate commands for your operating system or distribution. Here are some common examples for different platforms:
On Linux using systemd:
- To start the MySQL server, run: sudo systemctl start mysqld
- To stop the MySQL server, run: sudo systemctl stop mysqld
- To check the status of the MySQL server, run: sudo systemctl status mysqld
On Linux using init.d:
- If your distribution uses init.d scripts, you may use the following commands:
- To start the MySQL server: sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
- To stop the MySQL server: sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
- To check the status of the MySQL server: sudo /etc/init.d/mysql status
On macOS using Homebrew:
If you've installed MySQL using Homebrew, you can use the following commands:
- To start the MySQL server: brew services start mysql
- To stop the MySQL server: brew services stop mysql
- To check the status of the MySQL server: brew services list
On Windows using services:
On Windows, MySQL is usually installed as a service. You can control the MySQL service using the Services management console or the command prompt.
To start or stop the MySQL server via the Services management console:
- Open the Services management console by typing services.msc in the search bar or the Run dialog box.
- Find the MySQL service, usually named MySQL, MySQLxx or MySQL Server (where "xx" represents the version number).
- Right-click on the service and select "Start" or "Stop" as needed.
To start or stop the MySQL server using the command prompt:
- Open a command prompt with administrative privileges.
- To start the MySQL server, run: net start MySQL
- To stop the MySQL server, run: net stop MySQL
Each MySQL installation might have specific scripts, commands, or aliases to start or stop the server. Always refer to the documentation for your particular installation or distribution for more detailed information.
8. What are DDL, DML, and DCL?
These specific MySQL interview questions and answers for experienced candidates can be helpful. DDL stands for Data Definition Language in MySQL, and it is used in database schemas and descriptions to determine how data should be stored in the database.
DDL Queries:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- DROP
- TRUNCATE
- COMMENT
- RENAME
DML stands for Data Manipulation Language and is used to manipulate data in databases. It largely consists of standard SQL commands for storing, modifying, retrieving, deleting, and updating data.
DML Queries are:
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- MERGE
- CALL
- EXPLAIN PLAN
- LOCK TABLE
DCL stands for Data Control Language and encompasses instructions that deal with user rights, permissions, and other database system controls.
List of queries for DCL:
- GRANT
- REVOKE
9. What is the MySQL binary log, and how do you use it?
The MySQL binary log is a log file that records all changes to the database, such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements, as well as DDL statements. You can use the binary log for various purposes, such as replication, point-in-time recovery, auditing, and debugging. To use the binary log, you need to enable it and configure its settings.
10. What is a query in MySQL?
A query in MySQL is a question or request for data or information from a MySQL database. In other words, it is a way to interact with the database to perform various operations such as retrieving, inserting, updating, or deleting data. Queries in MySQL are typically written using SQL (Structured Query Language), which is a standardized language designed to communicate with relational databases.
A query typically consists of SQL commands, expressions, and operators that define criteria for how the database should search, filter, modify, or present the data.
11. What is a database schema?
A database schema is the blueprint or skeleton structure that represents the logical configuration of a database. It defines the organization and relationships between tables, as well as the columns, data types, constraints, indexes, and other elements that comprise the database.
In essence, a database schema is a high-level representation of how data is organized, stored, and related within the database. It plays a critical role in designing and maintaining database systems, as it allows developers and administrators to visualize the overall structure, identify redundancies, ensure normalization, and optimize performance.
Database schema can also be referred to as the formal definition of the database structure, which is typically designed, managed, and queried using SQL (Structured Query Language).
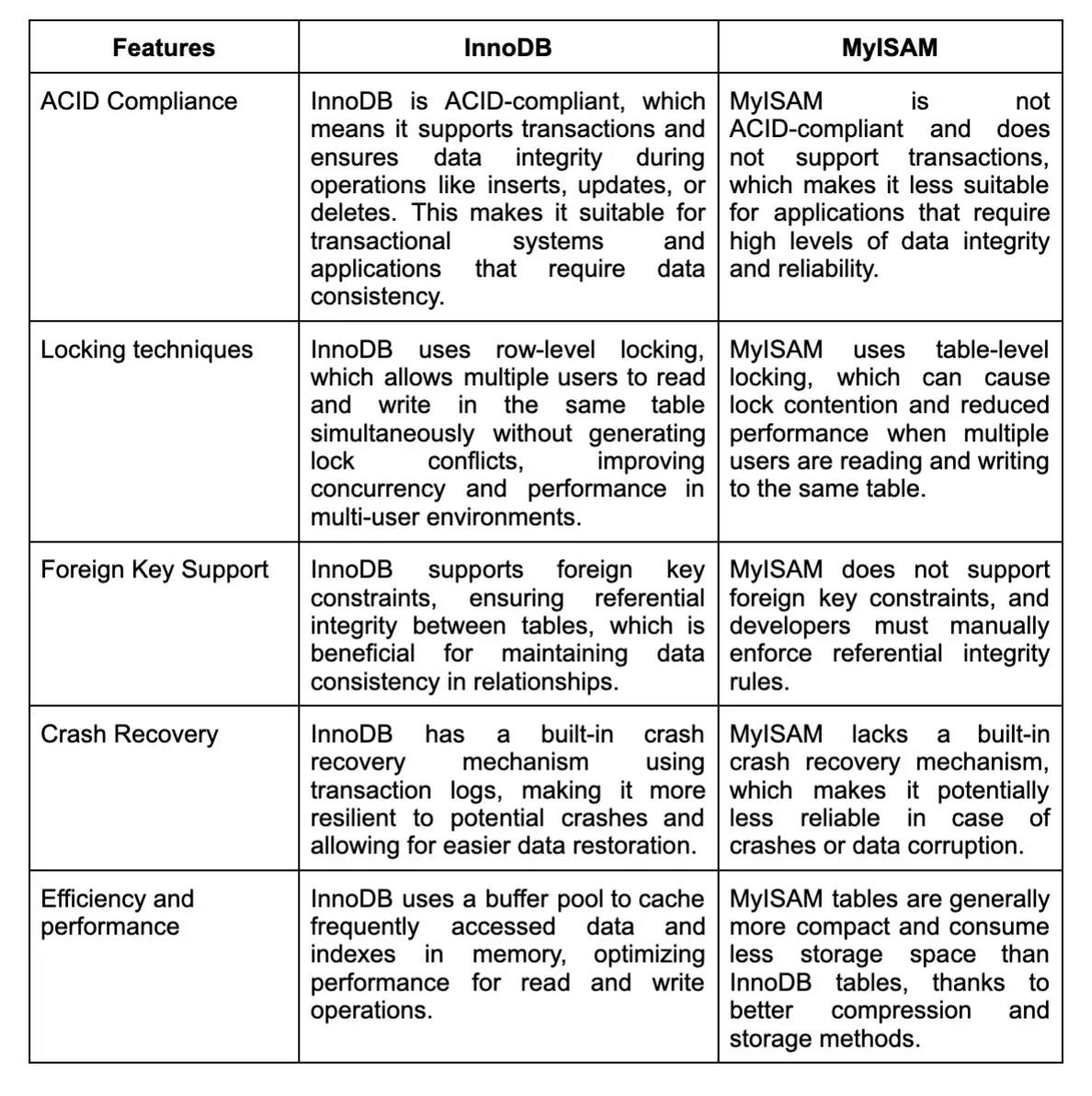
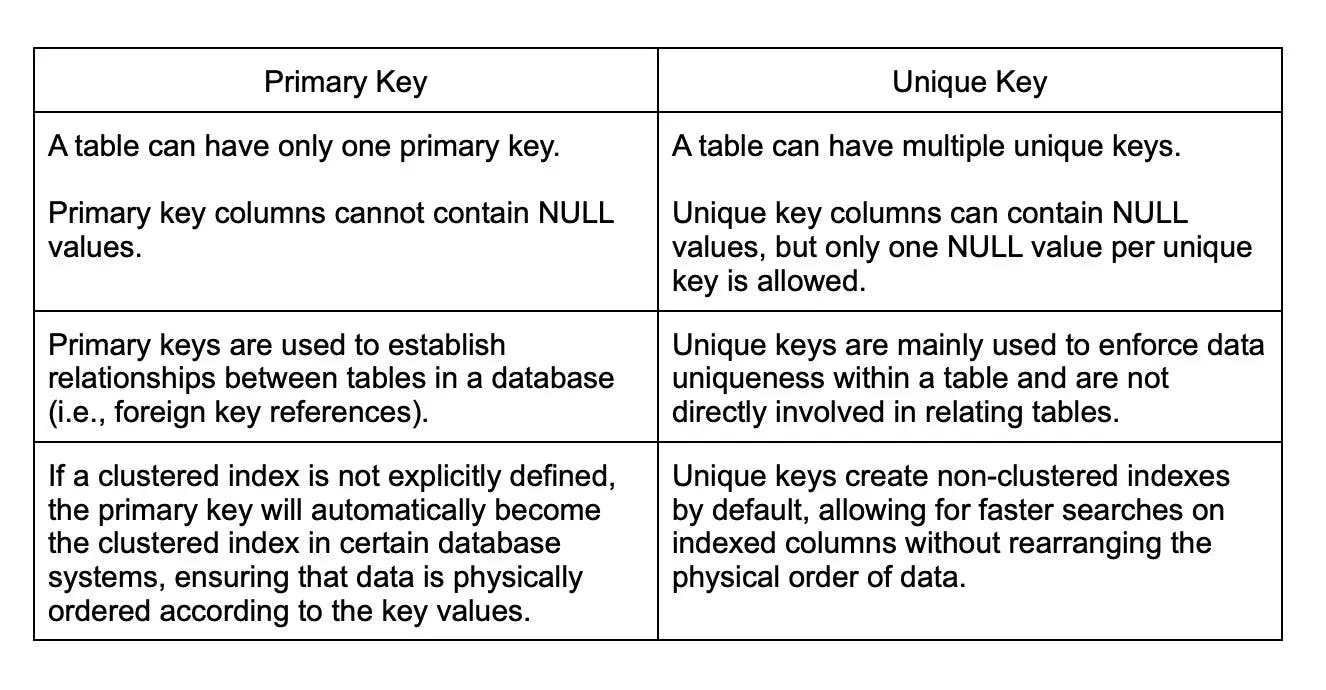
12. What is the difference between a primary key and a unique key?
Both primary key and unique key are used to enforce constraints and uniquely identify records in a MySQL table. However, there are some differences between the two:
13. What is a composite primary key?
A composite primary key, also known as a compound primary key or a concatenated primary key, is a primary key that is composed of two or more columns in a table. It is used when a single column is not sufficient to uniquely identify a row within the table.
By combining multiple columns, a composite primary key enforces uniqueness for the combination of those column values and ensures that every row in the table can be uniquely identified. It also maintains referential integrity in relationships with other tables that involve those columns.
14. What is a foreign key constraint?
A foreign key constraint is a rule that enforces referential integrity within a relational database by establishing a relationship between two tables. Specifically, the foreign key constraint ensures that the values in the foreign key column(s) of one table must match the corresponding values of the primary key column(s) in the related table.
A foreign key constraint has four main characteristics:
Establishes relationships: A foreign key in one table refers to the primary key of another table, creating a parent-child (referenced-referencing) relationship between them.
Maintains referential integrity: By requiring a match between the foreign key and primary key values, the constraint ensures that no orphan records are left in the child table, and that all child table rows have a valid parent in the parent table.
Controls cascading actions: Foreign key constraints can define cascading actions such as CASCADE, SET NULL, SET DEFAULT, and NO ACTION (or RESTRICT) for ON DELETE and ON UPDATE events. These actions determine how the foreign key columns in the child table should be affected when a referenced row in the parent table is deleted or updated.
Supports composite keys: A foreign key can reference multiple columns in the parent table's primary key. In this case, the set of columns in the child table that forms the foreign key is called a composite foreign key.
15. How do you update data in a table in MySQL?
To update data in a MySQL table, you can use the UPDATE statement. The basic syntax for the UPDATE statement includes the table name, the new values for each column, and a WHERE condition to identify the row(s) to be updated:
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;
The WHERE clause is optional but highly recommended to avoid updating all rows in the table unintentionally. When the WHERE clause is not used, the UPDATE statement will modify all rows in the specified table.
16. How do you delete data from a table in MySQL?
To delete data from a MySQL table, you can use the DELETE statement. The basic syntax for the DELETE statement consists of the table name and a WHERE condition to identify the row(s) to be deleted:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
The WHERE clause is optional but highly recommended to avoid deleting all rows in the table unintentionally. When the WHERE clause is not used, the DELETE statement will remove all rows from the specified table.
17. How do you retrieve data from a table in MySQL?
To retrieve data from a table in MySQL, you use the SELECT statement. The basic syntax for the SELECT statement includes the columns you want to retrieve, along with the table name and an optional WHERE condition to filter the data:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
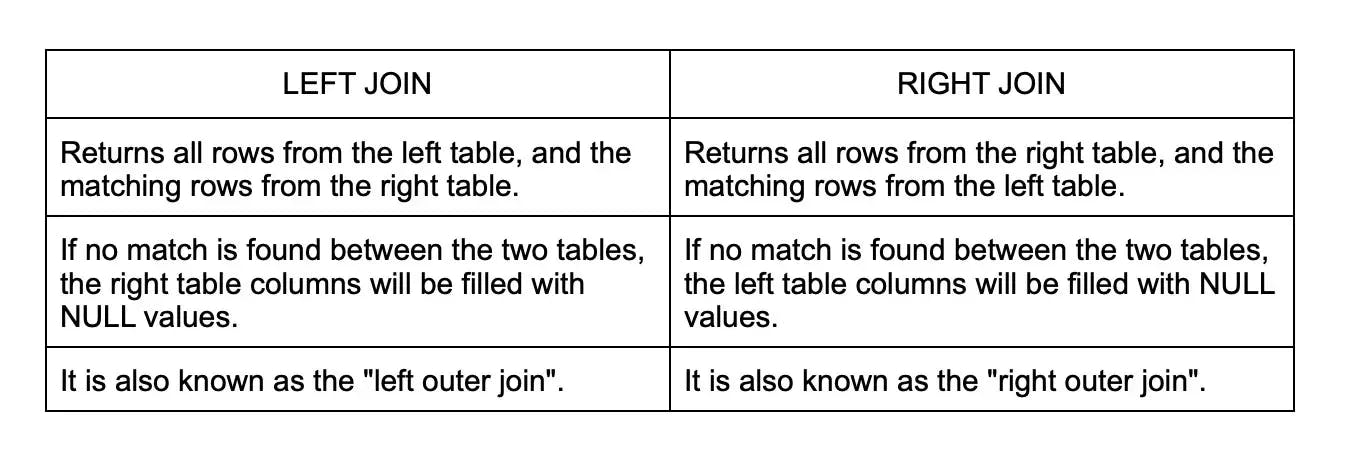
18. What is the difference between a left join and a right join?
In MySQL, both LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN are types of outer joins used to retrieve data from multiple tables. The difference between the two lies in how they handle non-matching rows. Here's a breakdown of their behavior:
19. What is the difference between a full outer join and a cross join?
A FULL OUTER JOIN and a CROSS JOIN are two different types of join operations in SQL that achieve different results.
A FULL OUTER JOIN combines the results of both LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN, returning all rows from both tables, even if there is no match between the joined columns. If there is no match, the resulting row will have NULL values for the non-matching columns.
A CROSS JOIN, also known as a Cartesian product, returns every possible combination of rows from the two joined tables, without any conditions. The result set will contain the total number of rows in Table1 multiplied by the total number of rows in Table2.
20. How do you add a new column to an existing table in MySQL?
To add a new column to an existing table in MySQL, you can use the ALTER TABLE statement followed by the ADD COLUMN keyword and the column definition. For example, to add a new column called "phone_number" to a table called "customers," you would use the following SQL statement: ALTER TABLE customers ADD COLUMN phone_number VARCHAR(20). This will add a new column to the "customers" table with a data type of VARCHAR and a maximum length of 20 characters.
21. What is the difference between a NULL value and a zero value in MySQL?
In MySQL, a NULL value and a zero value are conceptually different and serve distinct purposes:
NULL value: A NULL value represents the absence of a value or an unknown value for a specific column in a row. It signifies that the data is either missing, not applicable, or not collected. When a column contains NULL, it means it has no value, and any comparison or operation involving NULL typically results in NULL as well. For example, NULL + 1 = NULL.
Zero value: A zero value is an actual numeric value, indicating that the value of the specific column in a row is zero. Zero participates in arithmetic and comparison operations like any other number. It is a valid value for numeric data types such as INT, FLOAT, and DECIMAL and carries a distinct meaning when used in calculations. For example, 0 + 1 = 1.
It's essential to understand the difference between NULL and zero values to ensure that the database design, data integrity, and query results are accurate and meaningful.
22. How do you rename a table in MySQL?
You can rename a table in MySQL using the RENAME TABLE statement. The syntax for renaming a table is as follows:
RENAME TABLE old_table_name TO new_table_name;
Replace old_table_name with the current name of the table you want to rename, and new_table_name with the new name you want to assign to the table. For example, to rename a table called employees to staff, the command would be:
RENAME TABLE employees TO staff;
23. What is a database transaction?
A database transaction is a logical work unit that includes one or more database activities. It is a technique for combining many database operations into a single, atomic action that either succeeds or fails as a whole. Transactions guarantee that all database activities are carried out as a single, consistent unit, preserving data integrity.
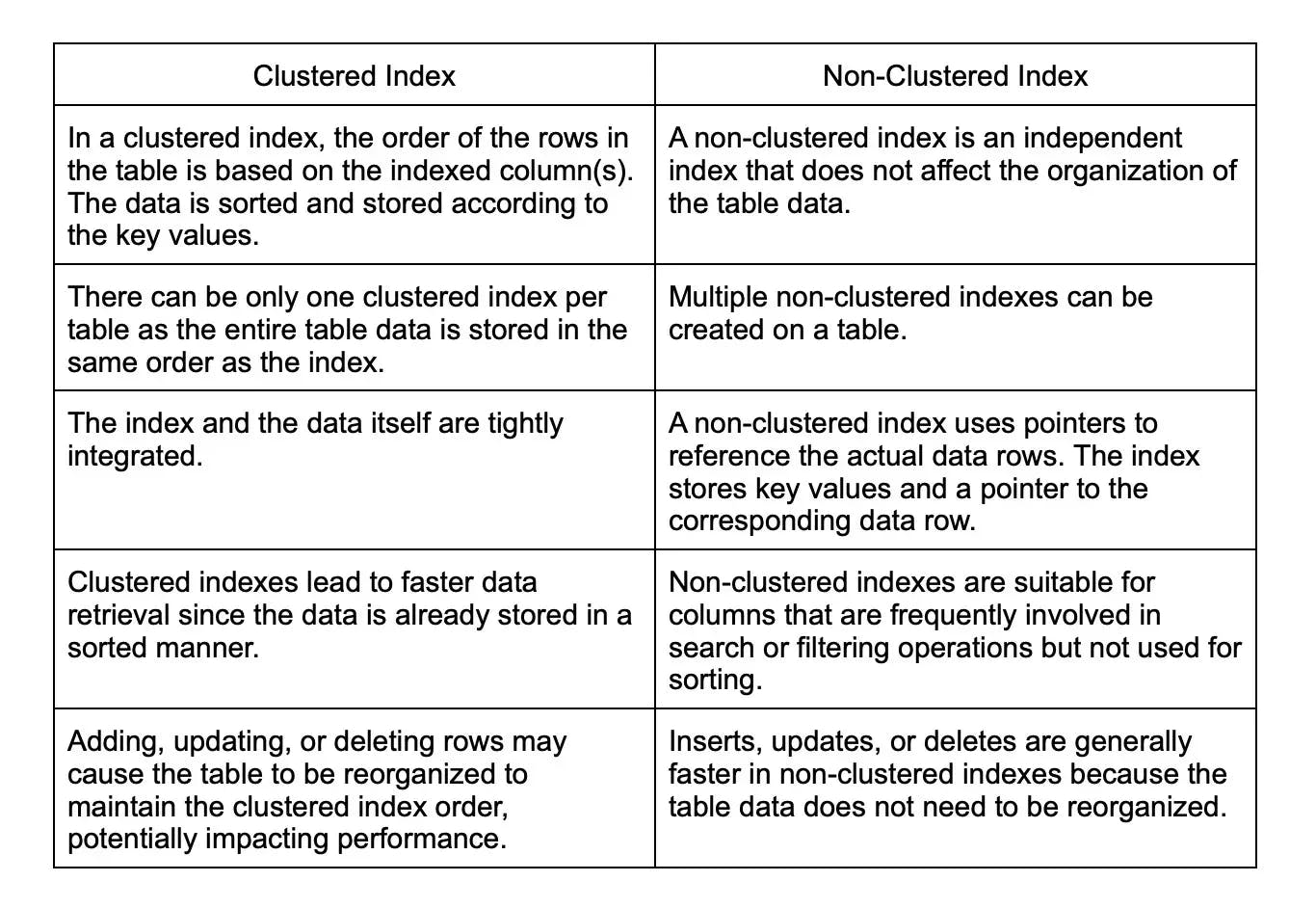
24. What is the difference between a clustered and a non-clustered index?
A clustered and a non-clustered index represent two types of indexing techniques used in database systems, and they have different structures and use-cases:
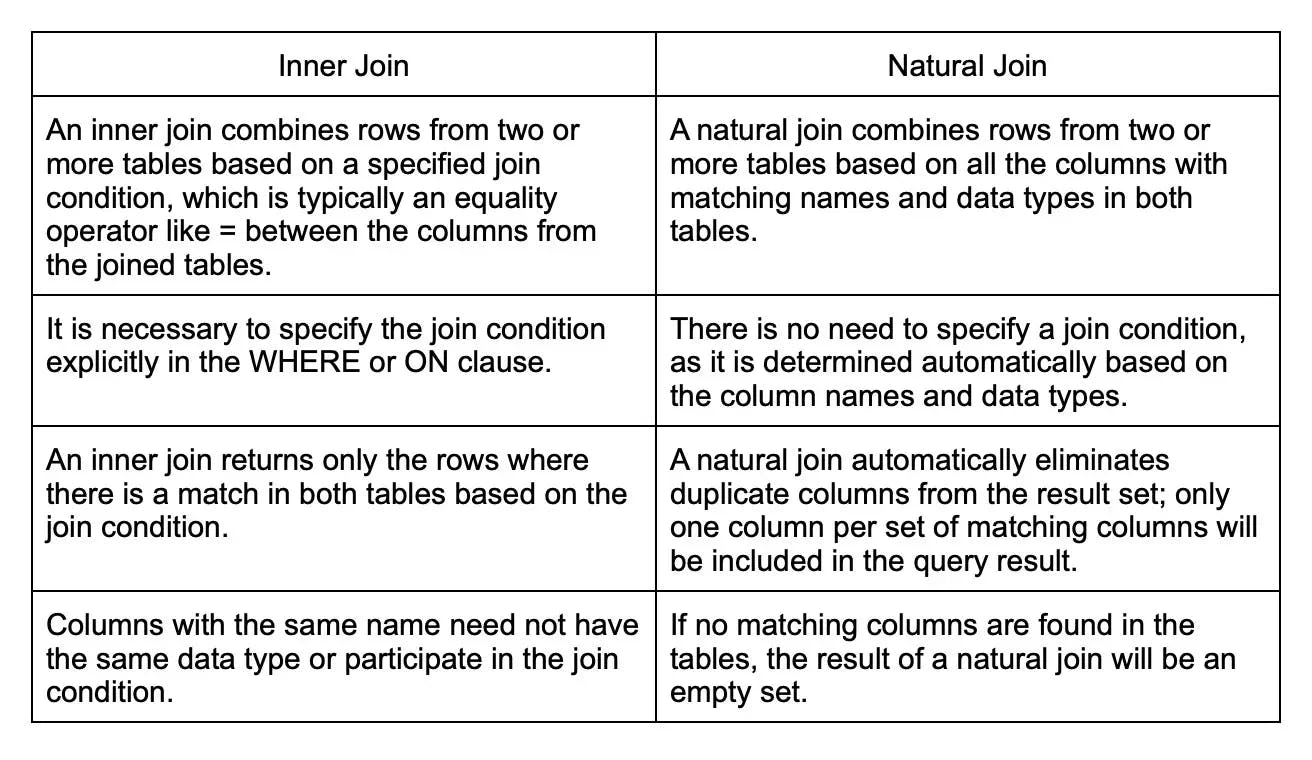
25. What is the difference between an inner join and a natural join?
The primary difference between an inner join and a natural join lies in the way they determine which columns to use for joining and how they handle duplicates. Here's a detailed comparison:
26. What is the difference between the CHAR and TEXT data types in MySQL?
The difference between the CHAR and TEXT data types in MySQL is their storage capacity, use case, and how they handle character length:
Storage Capacity: CHAR is typically used for storing short strings with a fixed length. The maximum length of a CHAR column can be 255 characters. On the other hand, TEXT is used for storing longer text data with variable lengths. It can store up to 65,535 characters.
Use Case: CHAR is suitable for storing data with known and consistent lengths, such as postal codes or country codes. TEXT is more appropriate for storing large chunks of text data, like paragraphs, comments, or descriptions, that can have variable lengths.
Character Length Handling: CHAR is a fixed-length data type, which means that it always uses the maximum defined length, and the unused characters are padded with spaces. In contrast, TEXT is a variable-length data type, using only the space required for the stored data without any padding.
Remember that both CHAR and TEXT are non-binary string data types and store character data. If you need to store binary data, you should use the corresponding binary types: BINARY for fixed-length and BLOB for variable-length data.
27. What is a subquery, and how do you use it in MySQL?
A subquery, also known as a nested query or inner query, is a query embedded within another query in MySQL. Subqueries are enclosed within parentheses and can be used within various SQL clauses, such as SELECT, FROM, WHERE, HAVING, and JOIN. They help in breaking down complex queries into simpler parts, increasing readability, and providing more flexibility in data manipulation and retrieval. Subqueries can return a single value (scalar subquery), a single row or column, or a table.
Here's an example of how you can use a subquery in MySQL:
Consider two tables: orders and customers. You want to find all customers who have placed an order worth more than the average order value.

In this example:
- The innermost subquery calculates the average order value across all orders.
- The middle subquery selects a flag (1) for all orders where the customer ID matches and the order value is greater than the calculated average.
- The outer query returns the customer ID and customer name for all customers who have at least one order that matches the conditions defined in the middle subquery.
28. What is a correlated subquery?
A correlated subquery is one that is run once for every row returned by the outer query. The subquery refers to a column from the outer query and utilizes it as a condition. A correlated subquery in MySQL can be used to extract data from one table depending on the values of another table.
29. How do you use the EXISTS operator in MySQL?
The EXISTS operator in MySQL is used in conjunction with a subquery to determine if the subquery returns any rows. The EXISTS operator returns TRUE if the subquery produces at least one row and FALSE if the subquery returns no rows. It is often used in the WHERE and HAVING clauses to filter results based on the existence of related records in other tables or based on specific conditions.
Here's an example of how you can use the EXISTS operator in MySQL:
Consider two tables: employees and projects. You want to find all employees who are working on at least one project.

30. What is a temporary table, and how do you create one in MySQL?
A temporary table in MySQL is a non-permanent table that is created to store intermediate results for complex queries or procedures, or used for a specific session or operation within the database. Temporary tables are automatically dropped when the user's session ends or when the connection is closed.
To create a temporary table in MySQL, use the CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE statement, followed by the table name and its columns along with their data types and constraints. Here's an example:

Wrapping up
If candidates know the correct answers to these questions, it demonstrates that they understand key features of MySQL, such as database architecture, querying, optimization, and security. Furthermore, the applicants are capable of dealing with tricky situations and ensuring the efficient functioning of MySQL databases.
If you're looking for experienced MySQL developers and don't want to compromise on quality, Turing's AI-powered talent cloud can help you onboard them in only a few clicks. Whether you need to construct strong database systems, optimize current databases, or solve difficult issues, our MySQL developers are ready to tackle any challenge right away.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber MySQL developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.