Linux
Basic Interview Q&A
1. What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source operating system based on the Unix platform. It was first created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and has since become one of the most popular choices for servers and embedded systems. With its stability, security, and flexibility, Linux allows users to customize and optimize their computing experience. It also supports a wide range of software and applications.
2. Why is Linux considered more secure than other operating systems?
Linux is considered more secure than other operating systems for several reasons. Firstly, Linux's open-source nature allows it to be examined and scrutinized by a vast community of developers worldwide, making it harder for potential vulnerabilities to go unnoticed.
Additionally, Linux's file and directory permissions system is stronger than that of other operating systems, granting users only the access they need to perform their tasks, and limiting the potential damage that could be done by a security breach.
Lastly, Linux distributions generally come with fewer software and components installed by default, reducing the overall attack surface of the system. All these features make Linux a solid choice for security-conscious users and organizations.
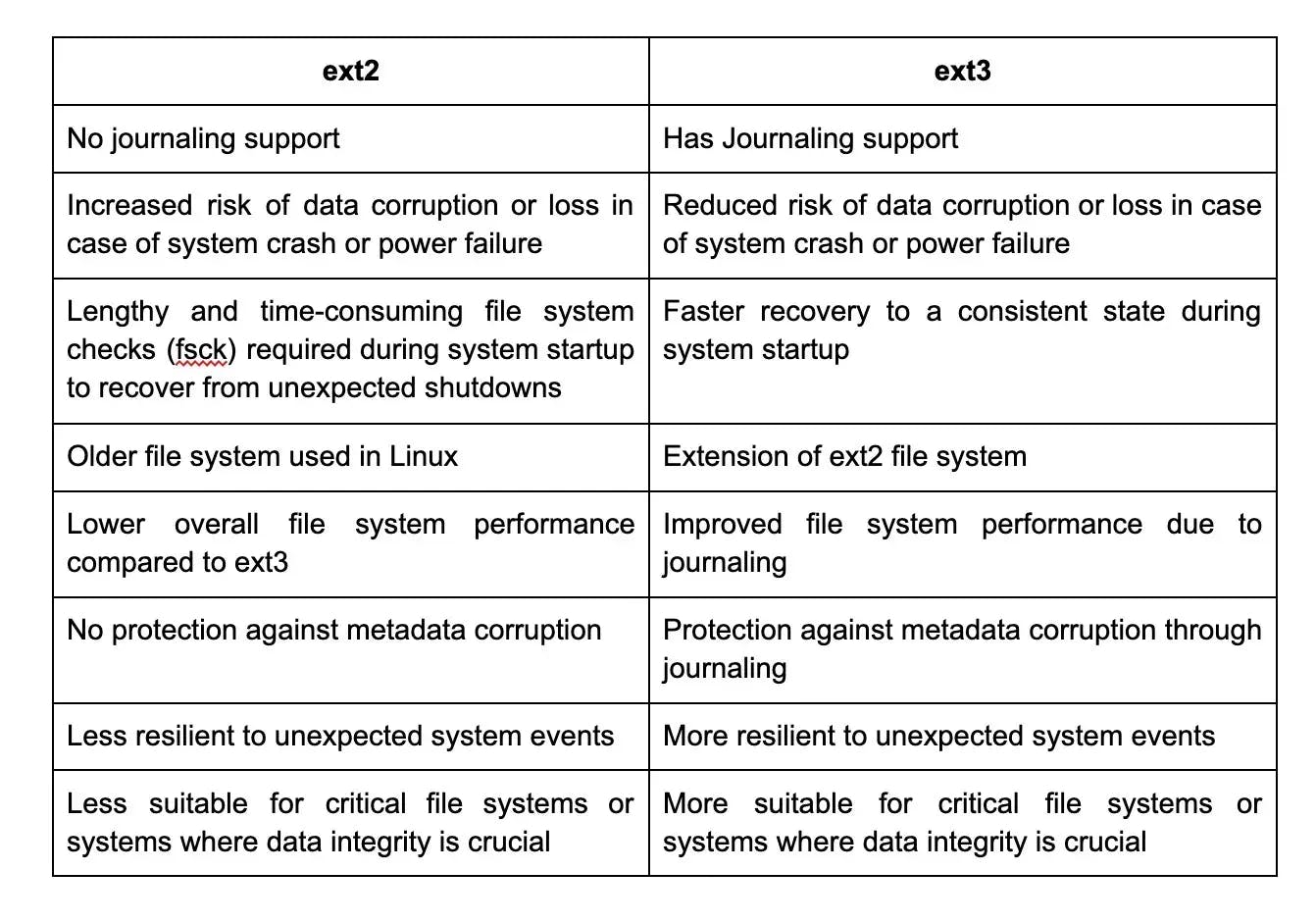
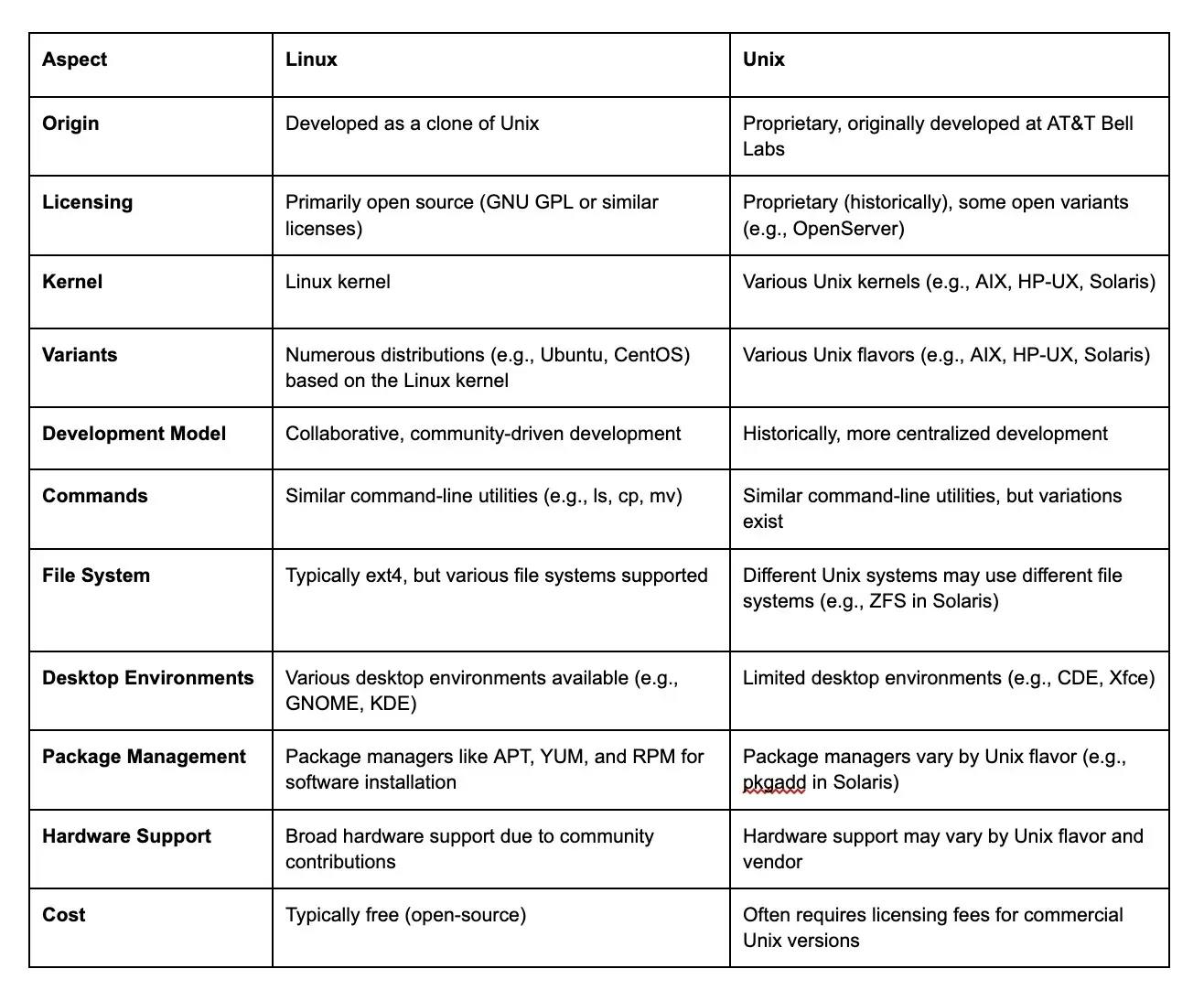
3. What is the difference between Linux and Unix?
4. What is the core of the Linux operating system?
The core of the Linux operating system is commonly referred to as the Linux kernel. It is responsible for managing system resources, providing essential services, and facilitating communication between hardware and software components. The Linux kernel is an open-source project developed by a global community of contributors, making it highly customizable and widely used in various devices, from smartphones to servers. The kernel controls the execution of programs, manages memory, handles input/output operations, and enables communication between different components of the system
5. How can you monitor system resource utilization on Linux? Provide a command to check CPU and memory usage.
You can use the top command to monitor system resource utilization. Here's how you can check CPU and memory usage. This command will display a real-time view of system statistics. To exit, press q.
6. What is BASH?
BASH is a command-line shell and scripting language primarily used in Unix-based systems, including Linux and macOS. It stands for "Bourne Again SHell," indicating its lineage from the original Bourne shell. BASH allows users to interact with the operating system by executing commands, managing files, and automating tasks through script files. It is a powerful and flexible tool for both beginners and advanced users.
7. What is LILO?
LILO is a boot loader for Linux operating systems that stands for "LInux LOader." It is responsible for loading the operating system kernel into memory and transferring control to it. LILO is one of the oldest boot loaders in use on Linux systems and has been largely replaced by GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) as the preferred boot loader due to its support for contemporary hardware and more advanced features.
8. Why is the GNU project important?
The GNU project was started with the goal of creating a free functioning framework for clients. Clients would be able to test, share, circulate, study, update, and improve the product, as well as bring out new features.
The goal of this project was to provide a free functional framework that included "everything valuable that generally accompanies a UNIX framework so that one could get by with no product that wasn't free."
Every other component of the Linux framework, with the exception of the piece, is GNU. It was taken under GNU variation 2 and the name Linux was changed to GNU/Linux as a result.
9. How can you check the current working directory in a Linux shell script and store it in a variable?

10. Mention the maximum length for a filename allowed in Linux.
Linux allows a maximum length of 255 characters for any filename, excluding the pathname. This furthest point does not include the pathname, therefore the total pathname and filename length might easily exceed 255 characters.
Make sure that you mention the exclusion of pathname, as in a Linux interview, the interviewer would definitely ask you about the pathname.
11. Why do we use LINUX?
There are several reasons why people choose to use the Linux operating system. To begin with, Linux is known for its stability and security, making it ideal for both personal and professional use. Additionally, Linux also provides a wide range of customization options, allowing users to tailor the system to their specific needs. Furthermore, Linux is an open-source platform, meaning that the source code is available to anyone who wants to modify or enhance it. This promotes a collaborative and innovative community, constantly improving the system. Lastly, Linux offers a variety of distributions, catering to different user preferences and requirements. Overall, Linux provides a powerful and flexible alternative to other operating systems.
12. Guide me through the Linux boot process, i.e, from when you press the power button to when the Linux login prompt appears.
These are the six stages of Linux boot process:
- BIOS: BIOS or Basic input/output system examines the integrity of the system and looks for the boot loader program on the CD-ROM or hard drive to load and run it. The BIOS grants control to the boot loader program after it has been discovered and loaded into memory. So, in a nutshell, the BIOS loads and executes the MBR bootloader.
- MBR: Master Boot Record (MBR) may be found on the bootable disk's first sector. Usually found in dev/hda or dev/sda. It contains GRUB-related information (Grand Unified Bootloader). So, in a nutshell, the MBR loads and runs the GRUB boot loader.
- GRUB: The default kernel image given in the grub configuration file is loaded by GRUB. /boot/grub/grub.conf is the location of the grub configuration file. It consists mostly of the kernel and the initrd image (initial ram disc - a method of loading a temporary root file system into memory). In a nutshell, GRUB loads and runs kernel and initrd images.
- Kernel: The root file system is mounted, and the /sbin/init program is run. The process id of init is 1 since it is the first program to be executed by the kernel. To double-check, run ps -ef | grep init.
- Init: Init determines the Linux run level by looking at the /etc/inittab file. In Linux, the following run levels are available:
halt
Single-user mode
Multi-user mode
Full Multi-user mode
Unused
X11
reboot
- Runlevel: Various services may be seen launching up as the Linux system is powering up. These are the runlevel programs, which are executed from the run level directory according to the run level's specifications.
13. How would you approach the problem of strengthening the security of password files?
In such Linux interview questions, make sure you talk about how you would approach and solve the problem. If you have any prior experience in solving such issues yourself, that would be a valuable addition in answering this Linux interview question.
/etc/passwd is a text file that Linux uses to store user account information. A one-way encrypted password is also stored in this file. It is accessible by numerous programs to obtain user information, posing a security concern; hence, the file must be 'Word Readable.' We may utilize the shadow password format to reduce the security risk. This approach stores account information in the /etc/passwd file on a regular basis.
The password, on the other hand, is saved as a single "x" character (not actually stored in this file). A second file, "/etc/shadow," stores encrypted passwords as well as other data such as account or password expiration values, and so on. Because the /etc/shadow file is only accessible by the root account, it poses less of a security concern.
14. In order to secure an ssh connection, what are the basic measures that you need to take?
Using ssh to connect to servers is extremely frequent. As a result, you can take the following measures to protect the SSH service:
- Disabling root login, as well as password-based logins, will improve the server's security.
- Disabling password-based logins and permitting key-based logins, which are safe but may be further restricted by only allowing access from specific IP addresses.
- Changing the default port to anything else reduces the number of random brute force attacks from the internet.
- By requiring the service to use only version 2 of the protocol, security and functionality enhancements will be introduced.
- The whitelist strategy may be used, where only people on a certain list are allowed to connect to the server through SSH.
15. What is the disadvantage of Open Source?
There are a few disadvantages of open source:
- One is the potential lack of support and troubleshooting. Since open source projects are often community-driven, there may not always be dedicated technical support available.
- Another disadvantage is the potential for security vulnerabilities if the open source software is not regularly maintained and updated.
- Lastly, open source may lack certain features or functionalities that proprietary software may have.
16. How does a system administrator know whether or not a user account is locked?
Run the following command in the shell to see if the user account is locked:
passwd –S
Another way is to look for the grep username in the /etc/shadow file, which will add a symbol '!' to the encrypted field in the password box.
Type the following command to simply unlock the password:
passwd –u
Run the following command twice, if there is a double exclamation mark:
usermod –U
17. List down the steps for how to find out Linux's memory use.
To find out how much memory Linux is using, use the "Concatenate" command in the Linux shell.
When you use this command, you'll get a list of memory usages by Linux, including Total Memory, Free Memory, Cache Memory, and many others. Other Linux commands include:
- $ free –m // this is the most basic command that displays memory use in megabytes
- $ vmstat –s // this command generates a virtual memory statistics report
- top // this command examines memory and CPU use
- htop // this command is very similar to the top command
18. What is Shell?
The Shell is a command line interpreter that allows you to interact with the computer's operating system. It provides a way for you to give instructions to the computer by typing commands. The Shell takes these commands and acts as a bridge between the user and the operating system, executing the commands and providing feedback and results. It is a powerful tool for managing files, running programs, and automating tasks.
19. How many types of Shells are there in Linux?
- Bash (Bourne Again SHell)
- Csh (C SHell)
- Tcsh (TENEX C Shell)
- Ksh (Korn SHell)
- Zsh (Z SHell)
Each shell has its own unique features and capabilities, so users can choose the one that best suits their needs and preferences.
20. What are the basic components of Linux?
Linux has three major components:
- The kernel which is responsible for managing hardware resources and memory allocation,
- The shell which is responsible for managing user input and output
- The utilities which provide additional functionality to interact with the kernel and shell.
These components work together to provide a robust and flexible operating system suitable for a wide range of applications and devices.
21. How can you change the permissions of a file named "file.txt" to give read, write, and execute permissions to the owner, and only read permission to others?
Assuming you want to give read, write, and execute permissions to the owner, and only read permission to others, you can use the following command:
chmod 750 file.txt
This command will set the permissions of "file.txt" as desired.The first digit (7) refers to the owner's permissions (read, write, and execute)
- The second digit (5) refers to the group permissions (read and execute only)
- The third digit (0) refers to the permissions for others (no permissions)
22. Create a symbolic link named "mylink" that points to a file named "target.txt" using the ln command.
To create a symbolic link named "mylink" that points to a file named "target.txt" using the ln command, you can use the following command:
ln -s target.txt mylink
This will create a symbolic link called "mylink" that points to the file "target.txt" in the current directory.
23. What is the GUI?
The GUI, or Graphical User Interface, is a visual interface that allows users to interact with a computer system through icons, menus, and windows. Instead of using command lines, a GUI provides a more user-friendly way to navigate and use software applications. It simplifies the user experience by using visual elements that are familiar and easy to understand.
24. Explain File Permissions types in Linux?
- Read: Allows a user to view the contents of a file.
- Write: Allows a user to modify the contents of a file.
- Execute: Allows a user to execute a file as a program.
These permissions can be assigned to three categories: owner, group, and others. Permissions can be viewed using the ls -l command and modified using the chmod command.
25. What are the environmental variables?
Environmental variables are dynamic values that can affect the behavior of software running on a system. They are stored in the operating system and can be accessed and modified by software applications. Common examples include the PATH variable, which tells the system where to look for executables, and the HOME variable, which defines the default user directory. Environmental variables are useful for customizing the software environment and improving compatibility.
26. What are the symbolic links?
Symbolic links, also known as soft links, are files that act as pointers to another file or directory within a file system. They are commonly used in Unix-based systems as a way to create shortcuts to files and directories, allowing for easier navigation and organization. A symbolic link appears to be a regular file or folder, but it only contains a path to the original file or folder, rather than actual data.
27. What are the hard links?
Hard links are file system links that point directly to an inode, or index node, of a file. They provide multiple directory entries for the same file, allowing it to be accessed from different locations. Unlike symbolic links, hard links do not maintain a separate file path; they refer to the same physical data. This means changes made to one hard link will be reflected in all other hard links to the same file.
28. What is redirection?
Redirection is the process of sending the output of a command to a file or another command instead of the default output destination (console). This allows you to save the output in a file for later use or to send it as input to another command.
29. What are Daemons?
In Linux, daemons are background processes that run continuously, providing specific services to other applications or users. They usually start during system boot and do not require any user intervention. Daemons are often used to handle network services, such as web servers (Apache), email servers (Postfix), or database servers (MySQL).
30. Describe the root account.
The root account is the highest level of administrative privileges in Linux. It has complete control over the system and can perform any task, including modifying system files, installing software, and creating/deleting user accounts. It is recommended to use the root account sparingly and instead use sudo (Superuser Do) to execute commands with elevated privileges.
31. Write a command to show the first 10 lines of a text file named "example.txt."
To show the first 10 lines of a text file named "example.txt" in Linux, you can use the head command with the -n option. Here's the command:
head -n 10 example.txt
This will display the first 10 lines of the "example.txt" file.
32. What are the different modes when using the vi editor?
When using the vi editor, there are three modes:
- Command mode: This is the default mode when you start vi. It allows you to navigate and operate on the text.
- Insert mode: In this mode, you can enter and edit text. Pressing the "i" key switches to insert mode.
- Visual mode: This mode is used for selecting or highlighting text. Pressing the "v" key switches to visual mode.
33. What are inode and process id?
The inode (index node) is a data structure in a Unix-like file system that stores information about a file, such as its permissions, size, modification time, and the location of its data blocks.
A process ID (PID) is a unique numeric identifier assigned to each running process in Linux. It is used by the operating system to track and manage processes. The PID is essential for performing process-related operations, such as sending signals or terminating a process.
34. What are the Process states in Linux?
In Linux, a process can be in one of the following states:
- Running: The process is actively executing on the CPU.
- Sleeping: The process is waiting for an event, such as I/O completion.
- Stopped: The process has been stopped, either by a user or a signal.
- Zombie: The process has completed execution but still has an entry in the process table. It is waiting for its parent process to acknowledge its termination.
35. Explain Process Management System Calls in Linux.
Process Management System Calls are a set of functions provided by the Linux kernel to manage processes. They include functions such as fork(), exec(), wait(), and kill(), which allow creating new processes, executing programs, waiting for process termination, and sending signals to processes.
36. What is a File system in Linux? Explain different file system types in Linux
A file system in Linux is a method used to organize and store files and directories on a storage device such as a hard disk. It provides mechanisms for creating, modifying, and deleting files, it also manages access permissions, file attributes, and directory structures.
There are several types of file systems in Linux, including,
- ext4: The default file system for most Linux distributions. It provides good performance, scalability, and support for large file sizes.
- ext3: The predecessor to ext4, it is compatible with ext4 and offers journaling for improved reliability.
- XFS: Designed for high-performance systems, XFS supports large storage and file systems. It includes features like online resizing and snapshot support.
- Btrfs: A copy-on-write file system with advanced features like RAID, snapshots, and volume management. It is still under development but offers experimental support in some distributions.
- NTFS: Although primarily used by Windows, Linux also has NTFS support to read and write files on NTFS partitions.
37. How can you mount a partition with the NTFS file system type in read-write mode in Linux?
To mount a partition with the NTFS file system type in read-write mode, you can use the mount command with the -o option. For example:
mount -t ntfs-3g /dev/sdX1 /mnt/ntfs
This command mounts the NTFS partition on /dev/sdX1 to the /mnt/ntfs directory in read-write mode using the ntfs-3g driver.
38. Why is LVM required?
Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is required in Linux for several reasons, like:
Flexibility: LVM provides a flexible approach to managing storage by abstracting physical disks and allowing for dynamic resizing of logical volumes without unmounting the file system.
Volume management: LVM simplifies storage management by providing features like volume grouping, resizing, snapshotting, and mirroring.
Storage efficiency: LVM enables the efficient utilization of available storage space by allowing logical volumes to span multiple physical disks.
39. What is umask?
Umask is a 3-digit octal value used to determine the default permissions for newly created files and directories in Linux. The mask value is subtracted from the base permission set to determine permissions.
40. How to set the mask permanently for a user?
To set the umask permanently for a user, the umask value can be modified in the user's shell profile configuration file such as .bashrc or .bash_profile. The umask value is set using the umask command with the desired octal value.
41. What is network bonding in Linux?
Network bonding, also known as link aggregation or NIC teaming, is a technique in Linux that allows multiple network interfaces to act as a single bonded interface. This provides increased bandwidth, fault tolerance, and load balancing.
42. What are the different modes of Network bonding in Linux?
The different modes of network bonding in Linux are:
- Mode 0 (Round-robin): Packets are transmitted sequentially over each bonded interface in a round-robin fashion.
- Mode 1 (Active-standby): One interface is active while the other is in standby mode for failover.
- Mode 2 (Load balancing): Load balancing is based on a hashing algorithm of source and destination MAC addresses, IP addresses, and port numbers.
- Mode 3 (Broadcast): All interfaces in the bond participate in transmitting and receiving packets.
- Mode 4 (IEEE 802.3ad): Implements the IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for dynamic link aggregation.
43. How to check the default route and routing table?
To check the default route and routing table in Linux, you can use the ip route show or netstat -nr command. These commands display the routing table, including the default route (0.0.0.0/0).
44. How to check which ports are listening in my Linux Server?
To check which ports are listening on a Linux server, you can use the netstat or ss command with appropriate options. For example, netstat -tuln or ss -tuln will display TCP and UDP listening ports.
45. Explain what a Linux kernel module is and provide an example of how to write one.
A Linux kernel module is a piece of code that can be dynamically loaded and unloaded into the Linux kernel at runtime, without requiring a reboot. It can extend or modify the kernel's functionality. Here's an example of a simple "Hello World" kernel module:

46. How to change the default run level in Linux?
The method to change the default run level in Linux depends on the distribution. In most modern distributions that use systemd, you can use the systemctl command to change the default run level. For example, to set the default run level to multi-user.target (equivalent to runlevel 3), you can use the command sudo systemctl set-default multi-user.target. In older distributions that use SysV init, you can modify the /etc/inittab file to change the default run level.
Wrapping up
All of the basics, fundamentals, and advanced subjects required for a Linux interview have been addressed in the article above. This, however, is not the end. Knowing how to answer/prepare for Linux developer jobs isn't enough; soft skills and team management are the second most crucial tools in your toolbox. As a candidate, you must be prepared to answer any soft skills questions in order to increase your chances of passing any technical interview, whether it is a Linux interview or another. You should discuss your projects, whether they are collaborative or personal, as well as how well you manage your time and team. As a recruiter, finding the appropriate applicant who is a good match for your firm is critical.
You can apply at Turing if you believe you are prepared to answer the Linux interview questions and answers as well as the soft-skills questions. Also you can message Turing if you want to add skilled Linux developers to your team.
Hire Silicon Valley-caliber Linux developers at half the cost
Turing helps companies match with top quality remote JavaScript developers from across the world in a matter of days. Scale your engineering team with pre-vetted JavaScript developers at the push of a buttton.
Tired of interviewing candidates to find the best developers?
Hire top vetted developers within 4 days.
Leading enterprises, startups, and more have trusted Turing

Check out more interview questions
Hire remote developers
Tell us the skills you need and we'll find the best developer for you in days, not weeks.